Kidney Disease Awareness
Jun 06, 2019 • 31 views
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs present in all vertebrates. They remove waste products from the body, maintain balanced electrolyte levels, and regulate blood pressure.
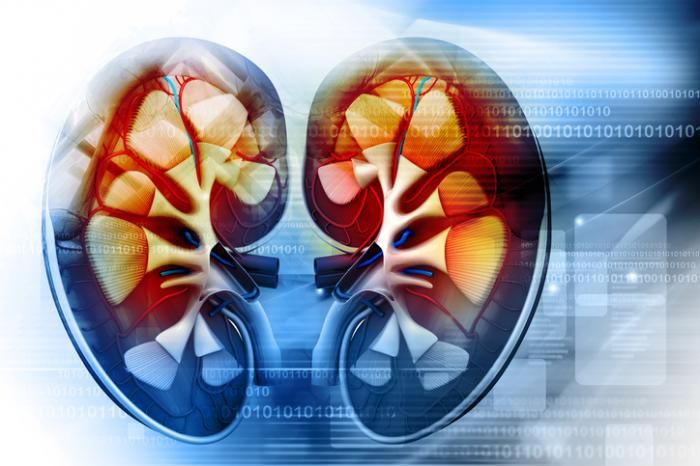
The kidneys are at the back of the abdominal cavity, with one sitting on each side of the spine.
Each kidney weighs 125–170 grams (g) in males and 115–155 g in females.
A number of diseases can affect the kidneys.
Diabetic nephropathy
In people with diabetic nephropathy, damage occurs to the capillaries of the kidney as a result of long-term diabetes.
Symptoms do not become clear until years after the damage starts to develop.
They include:
nausea
swollen legs
itchy skin
Kidney stones
Stones can form as a solid build-up of minerals in the kidney.
They can cause intense pain and might affect kidney function if they block the ureter.
Kidney infections
These tend to result from bacteria in the bladder that transfer to the kidneys.
Symptoms include lower back pain, painful urination, and sometimes fever. Changes in the urine may include the presence of blood, cloudiness, and a different odor.
Kidney infections are more common in women than in men, as well as in women who are pregnant. The infection often responds well to anitibiotics.
And there are many more kidney disease. But here are some few things that you can follow to protect yourself from these kidney diseases:
Control your blood sugar if you have diabetes.
Keep a healthy blood pressure.
Follow a low-salt, low-fat diet.
Exercise at least 30 minutes on most days of the week.
Keep a healthy weight.
Do not smoke or use tobacco.
Limit alcohol.
Drink plenty of water.


