Augmented Reality
Feb 03, 2019 • 23 views
Augmented Reality is the incorporation of digital details with the user's real atmosphere immediately. Augmented Reality uses the existing atmosphere and overlays new details about top of it.It is an enhanced version of reality where live direct or indirect views of physical real-world environments are augmented with superimposed computer-generated images over a user’s view of the real-world, thus enhancing one’s current perception of reality.
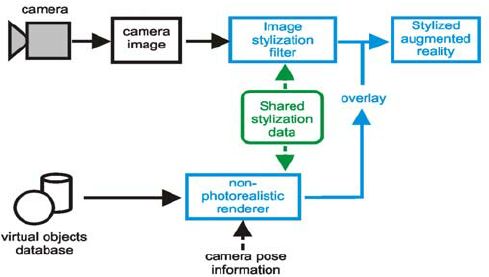
Augmented realityappsare written in special 3D programs that allow the developer to tie animation or contextual digital information in the computer program to an augmented reality "marker" in the real world. When a computing device's AR app or browserplug-inreceives digital information from a known marker, it begins to execute the marker's code and layer the correct image or images.
AUGMENTED REALITY VS VIRTUAL REALITY
Augmented Reality is rather different from virtual reality. Virtual reality means computer-generated environments for you to interact with, and be immersed in. Augmented reality (also known as AR),adds tothe reality you would ordinarily see rather than replacing it.As both virtual and real worlds harmoniously coexist, users of augmented reality experience a new and improved natural world where virtual information is used as a tool to provide assistance in everyday activities.

TYPES OF AUGMENTED REALITY
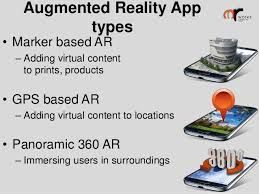
Marker Based Augmented Reality - :It uses a digicam and some kind of visible marking, such as a QR/2D rule, to build a consequence only when the marking is felt by a audience. Marker based programs use a digicam on the system to differentiate a marking from any other real life item. Unique, but simple styles (such as a QR code) are used as the indicators, because they can be easily identified and do not require a lot of handling power to study. The place and alignment is also measured, in which some kind of content and/or information is then overlaid the marking.
Markerless Augmented Reality - :As one of the most generally applied programs of Augmented Reality, markerless (also called location-based, position-based, or GPS) enhanced truth, uses a GPS, digital compass feature, speed gauge, or accelerometer which is included in the device to give data centered on your place. A strong power behind Markerless Augmented Reality technology is the wide accessibility of mobile phones and place recognition features they offer. It is normally used for applying guidelines, finding close by businesses, and other location-centric mobile apps.As one of the most generally applied programs of Augmented Reality, markerless (also called location-based, position-based, or GPS) enhanced truth, uses a GPS, digital compass feature, speed gauge, or accelerometer which is included in the device to give data centered on your place. A strong power behind Markerless Augmented Reality technology is the wide accessibility of mobile phones and place recognition features they offer. It is normally used for applying guidelines, finding close by businesses, and other location-centric mobile apps.
Projection Based Augmented Reality - :Projection based augmented reality works by projecting artificial light onto real world surfaces. Projection basedaugmented reality applicationsallow for human interaction by sending light onto a real world surface and then sensing the human interaction (i.e. touch) of that projected light. Detecting the user’s interaction is done by differentiating between an expected (or known) projection and the altered projection (caused by the user’s interaction). Another interesting application of projection based augmented reality utilizes laser plasma technology to project athree-dimensional (3D) interactive holograminto mid-air.
Superimposition Based Augmented Reality - :Superimposition based augmented reality either partially or fully replaces the original view of an object with a newly augmented view of that same object. In superimposition based augmented reality, object recognition plays a vital role because the application cannot replace the original view with an augmented one if it cannot determine what the object is.
