Ultrasound...
Feb 14, 2019 • 4 views
Ultrasound is a type of imaging system. It uses high-frequency sound waves to look at organs and structures inside the body. Health care professionals use it to view the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, liver, and other organs. During pregnancy, doctors use ultrasound to view the fetus.Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the body. It is used to help diagnose the causes of pain, swelling and infection in the body’s internal organs and to examine a baby in pregnant women and the brain and hips in infants. It’s also used to help guide biopsies, diagnose heart conditions, and assess damage after a heart attack. Ultrasound is safe, noninvasive, and does not use ionizing radiation.
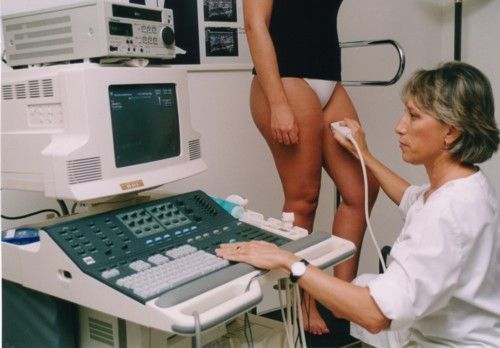
This procedure requires little to no special preparation.During an ultrasound test, you lie on a table. A special technician or doctor moves a device called a transducer over part of your body. The transducer sends out sound waves, which bounce off the tissues inside your body. The transducer also captures the waves that bounce back. The ultrasound machine creates images from the sound waves.ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels
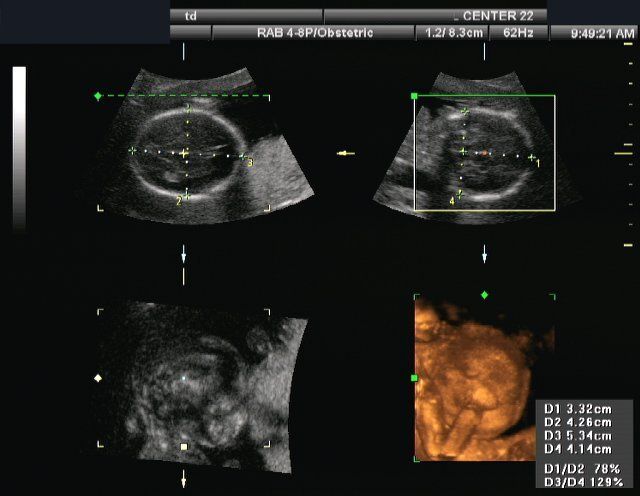
Conventional ultrasound displays the images in thin, flat sections of the body. Advancements in ultrasound technology include three-dimensional (3-D) ultrasound that formats the sound wave data into 3D images.
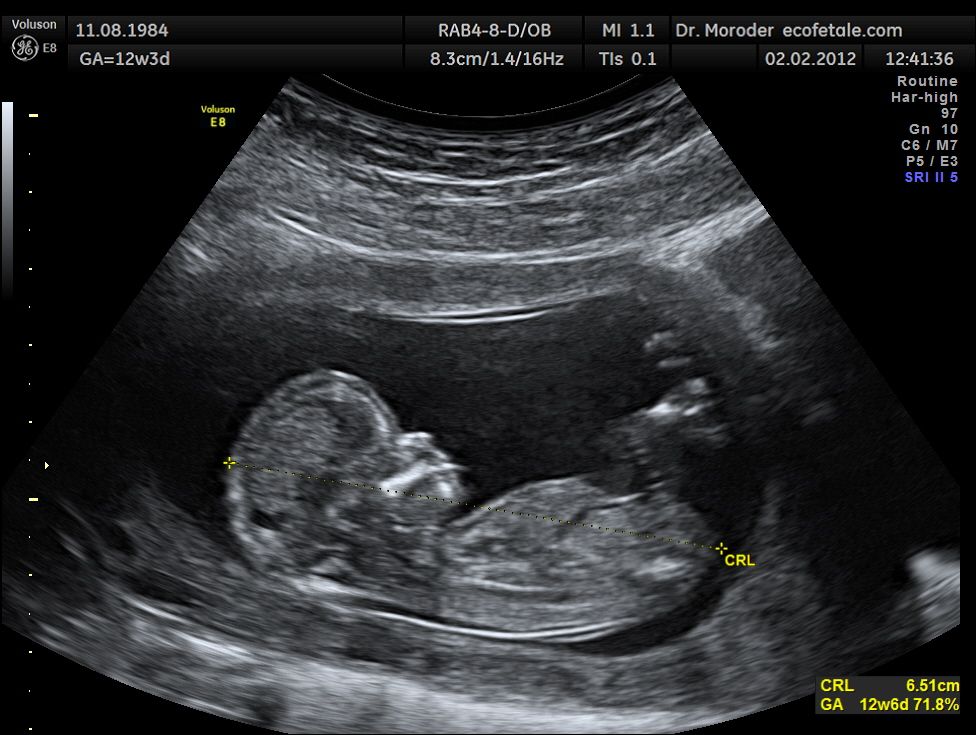
DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
A Doppler ultrasound study may be part of an ultrasound .Doppler ultrasonography, is a special ultrasound technique that allows the physician to see and evaluate blood flow through arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs, neck and/or brain (in infants and children) or within various body organs such as the liver or kidneys.
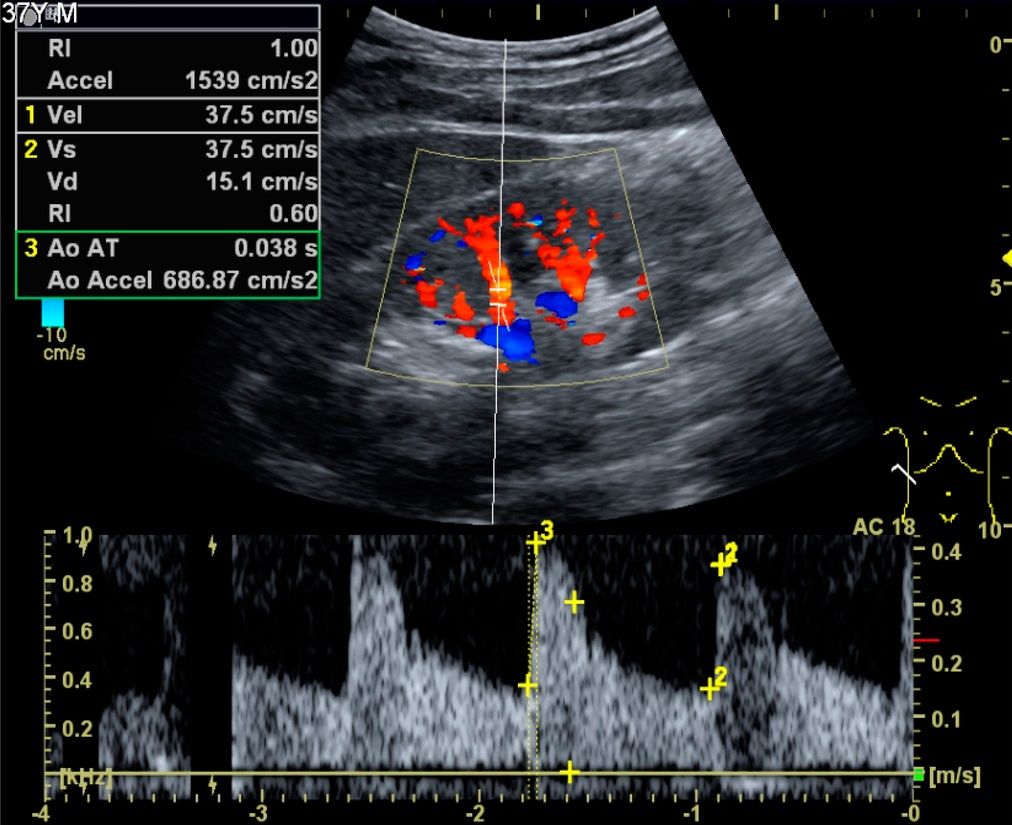
There are 3types of Doppler ultrasound:
Color Doppler
Power Doppler
Spectral Doppler
Ultrasound is used to help physicians evaluate symptoms such as:
pain
swelling
infection
Ultrasound is a useful way of examining many of the body's internal organs, including but not limited to the:
heart and blood vessels, including the abdominal aorta and its major branches
liver
gallbladder
spleen
pancreas
kidneys
bladder
uterus, ovaries, and unborn child (fetus) in
pregnant patients
eyes
thyroid and parathyroid glands
scrotum (testicles)
brain in infants
hips in infants
spine in infants
Benefits
Most ultrasound scanning is noninvasive (no needles or injections).
Occasionally, an ultrasound exam may be temporarily uncomfortable, but it should not be painful.
Ultrasound is widely available, easy-to-use and less expensive than other imaging methods.
Ultrasound imaging is extremely safe and does not use any ionizing radiation.
Ultrasound scanning gives a clear picture of soft tissues that do not show up well on x-ray images.
Ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality for the diagnosis and monitoring of pregnant women and their unborn babies.
Ultrasound provides real-time imaging,making it a good tool for guiding minimally invasive procedures such as needle biopsies
Drawbacks
Ultrasound waves are disrupted by air or gas; therefore ultrasound is not an ideal imaging technique for air-filled bowel or organs obscured by the bowel.
In most cases, barium exams, CT scanning, and MRI are the methods of choice in such a setting.
Large patients are more difficult to image by ultrasound because greater amounts of tissue attenuate (weaken) the sound waves as they pass deeper into the body and need to be returned to the transducer for analysis.
Ultrasound has difficulty in penetrating bone and, therefore, can only see the outer surface of bony structures .
