Radiation Protection...
Feb 07, 2019 • 21 views

The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation.
Many somatic dangers of radiation became evident a few months after x rays were discovered. Between 1911 and 1914, three review articles identified 54 cancer deaths and 198 cases of radiation induced malignancy. A few individuals cried out for radiation controls,but their voices against radiation harms was largely ignored. But when medical community became alarmed,finally in 1921 the first official action was taken when the British X ray and radium protection community was founded to investigate methods for reducing exposures.
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION
Radiation can harm biological systems by damaging the DNA of cells. If this damage is not properly repaired, the cells may divide in an uncontrolled manner and cause cancer.
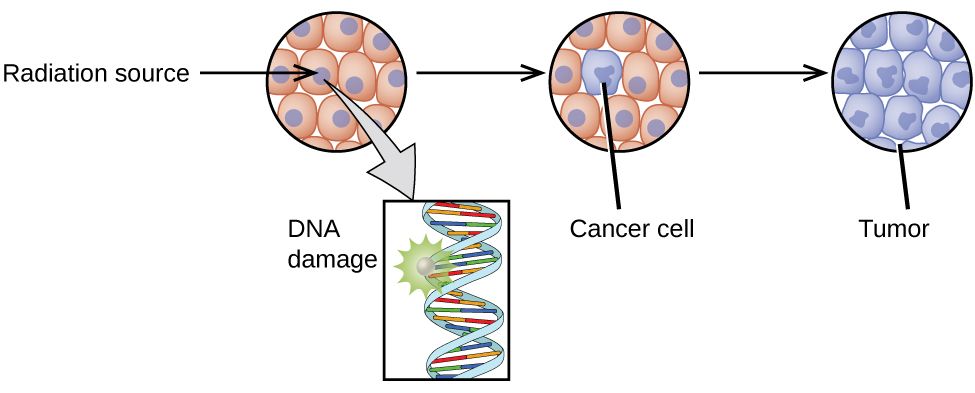
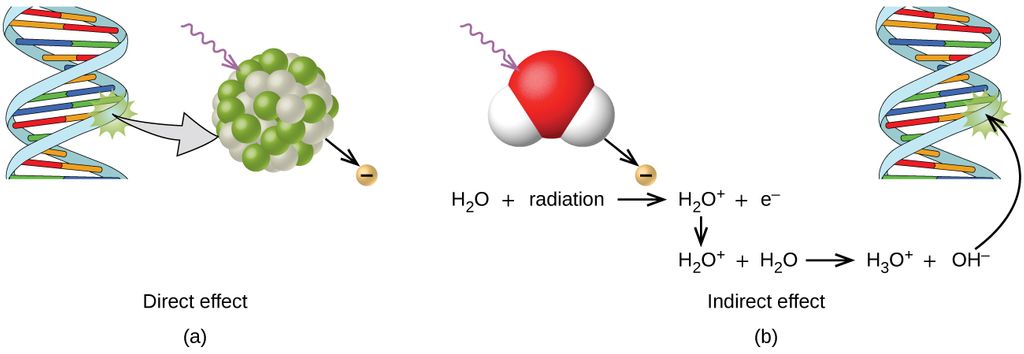
Ionizing radiation can (a) directly damage a biomolecule by ionizing it or breaking its bonds, or (b) create an H2O+ ion, which reacts with H2O to form a hydroxyl radical, which in turn reacts with the biomolecule, causing damage indirectly.
Radiation can harm either the whole body (somatic damage) or eggs and sperm (genetic damage).
Its effects are more pronounced in cells that reproduce rapidly, such as the stomach lining, hair follicles, bone marrow, and embryos.
2.Measuring Radiation Exposure
Several different devices are used to detect and measure radiation, including

The Geiger counterdetects and measures radiation. Radiation causes the ionization of the gas in a Geiger-Müller tube. The rate of ionization is proportional to the amount of radiation.
A scintillation counter contains a scintillator—a material that emits light (luminesces) when excited by ionizing radiation—and a sensor that converts the light into an electric signal.
Radiation dosimeters also measure ionizing radiation and are often used to determine personal radiation exposure. Commonly used types are electronic, film badge, thermoluminescent, and quartz fiber dosimeters.
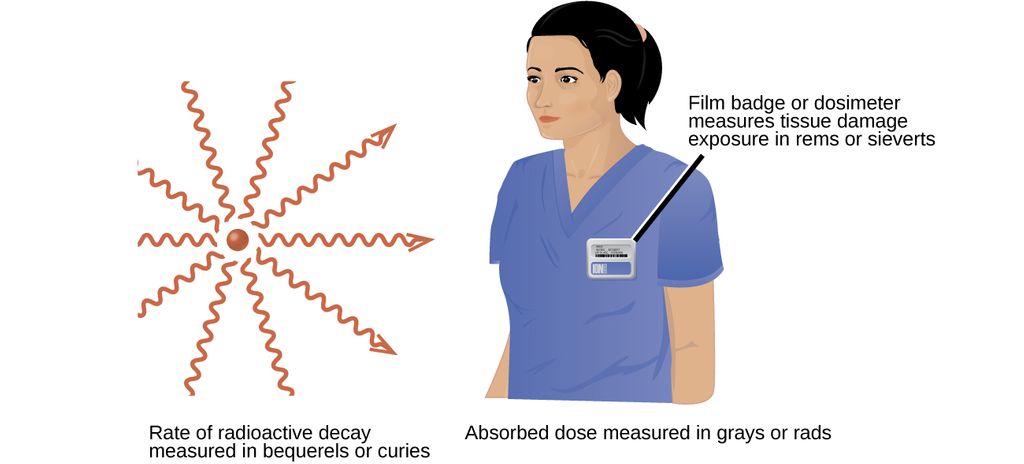
The effects of radiation depend on the type, energy, and location of the radiation source, and the length of exposure.
3.PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION PROTECTION
There are three principles of radiation protection practiced in radiology for dealing with live sources of radiation.
These three principles are called the Cardinal Rules of radiation protection; they are: time, distance, and shielding from ionizing radiation
Radiation protection is done with the help of lead this helps to stop ionising radiation to not to penetrate from the sources
4.Examples of RADIATION PROTECTION DEVICES….
LEAD APRON
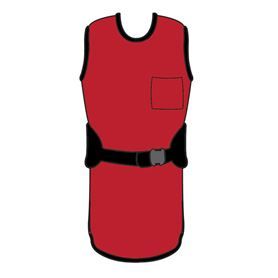
LEAD GLOVES
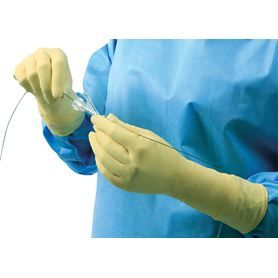
LEAD GOGGLES
THYROID SHIELD

BARRIER AND TABLE SHIELD