Child Labour In India
Oct 01, 2019 • 789 views
What is Child labour?
The International Labor Organization (ILO) characterizes child work as work that denies offspring of their youth, their potential and their poise, and that is destructive to their physical and mental improvement.
Be that as it may, youngsters or teenagers who take an interest in work that doesn't influence their wellbeing and self-improvement or meddle with their tutoring, isn't child labour. Model: helping their folks at home, helping family or gaining pocket cash outside school hours and on vacation.
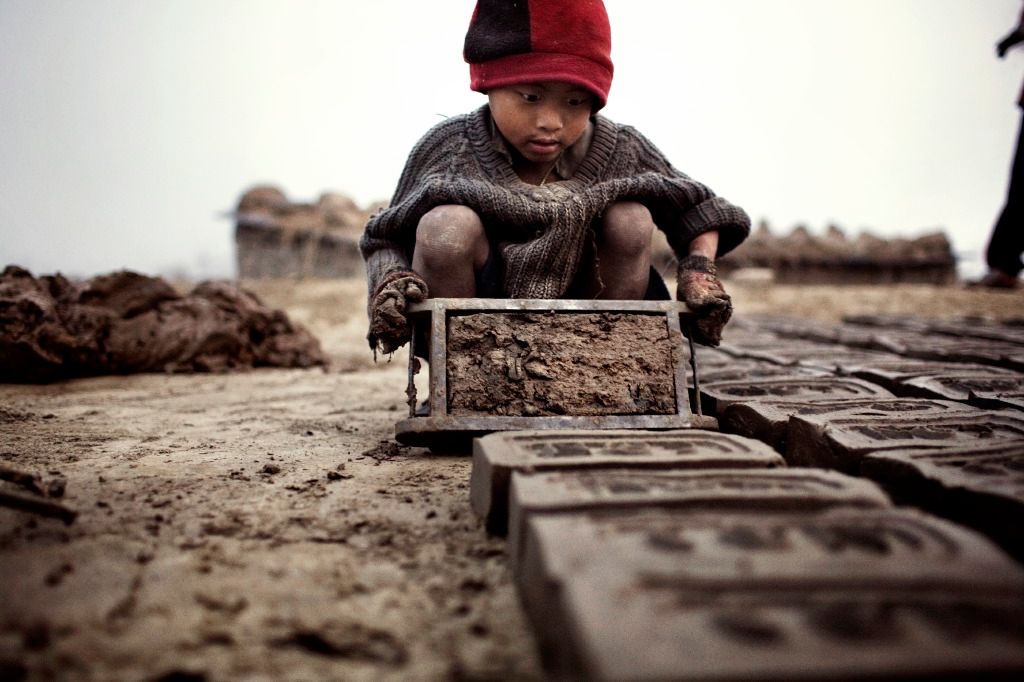

Child Labour Source: Witness Image
Child Labor in India-Statistics:
As indicated by the 2011 Census, there were more than 10.2 million "financially active" kids in the age gathering of 5to 14-5.6 million young boys and 4.5 million young girls.

Child Labour Statistics Source: UNICEF India
Child work has diminished in provincial zones notwithstanding; it has expanded definitely in the urban territories
An examination (2016) by CRY (Child Rights and You) of statistics information demonstrates that the general decline in child unjust work is just 2.2%per year from 2001 to 2011.
There are five states which are India's greatest child unjust work managers Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
Nature of Child Labour in India:
Gender: The division of work is sex explicit with young girls being occupied with increasingly local and locally established work, and young boys functioning as pay workers.
Bonded child unjust work: Bonded work implies the work of an individual against a credit or obligation or social commitment by the group of the youngster or family in general. bonded kid workers are regularly found in agriculture division or helping their families in block ovens, and Mine quarries. The Bonded Labor Liberation Front evaluates 10 million reinforced kids in India.
Change in Location of work: There has been an expanding association of kids in locally established works and in the informal segment. The adjustment in kind of kid work fundamentally credits to authorization of enactment and mindfulness among purchasers about youngster abuse.
Migrant kids: Migrant kids are frequently compelled to drop-out schools and are unavoidably given something to do at work-destinations.
Nature of work in Rural-Urban Areas: In urban regions, an enormous number of kids are occupied with manual residential work, cloth picking, eateries, engine repair shops and so on. In rustic division kids are occupied with the agrarian part including cotton developing, at glass, coordinate box and metal and lock-production plants, in weaving, cloth picking, beedi-making, in the rug making industry, in mining and stone quarrying, block ovens and tea gardens among others.
Reasons for Child Labour:
Neediness and Indebtedness: Indebtedness is the best reason for kid work. For devastated families, pay from a kid's work is typically vital for their own endurance or for that of the household. Children are additionally clung to work because of a family obligation. Country destitution and urban movement additionally frequently opens youngsters to being dealt for work
Grown-up joblessness and under-unemployment: high predominance of grown-up joblessness and under-business frequently power kids to work to help family.
Absence of education and Ignorance of youngster's folks: Illiteracy of the kid's folks further declines the circumstance. Ignorance and Lack of familiarity with the unsafe impacts of kid work cause them to damage the law and put their youngsters under the danger of barbaric abuse.
Absence of access to fundamental and important quality instruction and abilities preparing: The predominant instructive foundation is exceptionally unsatisfactory to offspring of financially denied families. Further miserable nature of training has prompted expanding dropout rates and constrained youngsters into child unjust work.
Mandatory training doesn't cover 15-18 age gathering. In any case, being uneducated or school dropouts, these youngsters are defenseless and regularly abused as a feature of casual, incompetent and easygoing workforce.
Demand for child unjust work: Increasing interest for child unjust labour particularly in urban regions is a significant explanation of commonness and increment in child labour. Youngsters are utilized in light of the fact that they are modest and adaptable as per the requests of the business and not mindful of their privileges.
Cultural elements: A desire that youngsters ought to add to the financial endurance of the family and network, just as the presence of huge families add to commonness of child unjust labour. Youngsters regularly take up family's customary work since the beginning. For instance, a Goldsmith's child takes to gold-smithery, or a craftsman's kid takes up carpentry since the beginning
Social elements: There is a solid relationship between India's segregated social structure and youngster work. Most of child workers in India have a place with the purported lower ranks (SCs), the ancestral and Muslim religious minority.
Effect of Prevalence of Child Labor:
Youngster work obstructs kids from picking up the abilities and instruction they have to have chances of tolerable work as a grown-up.
Child unjust work denies an offspring of his/her youth. It denies his/her entitlement to instruction yet in addition ideal to relaxation
Youngster workers face significant wellbeing and physical dangers: they work extended periods and are required to perform undertakings for which they are physically and formatively ill-equipped. Working in risky conditions antagonistically influences a child's physical and emotional well-being and debilitates scholarly, enthusiastic and mental advancement.

Effects of Child Labour Source: Slide Share
Destitution: Child work is both a reason and result of neediness. Family neediness forces youngsters into the work market to earn cash. In this way the kids pass up a chance to increase training, further sustaining family destitution crosswise over ages
Prevalence of an enormous number of child workers has long haul impact on the economy; it is a genuine hindrance to financial welfare of a nation.
Suggestions
Legitimate execution of Child Labor (Prohibition and Regulation) Act
Stricter discipline and punishment for one who utilizes or exercises child work
Improvement of instructive foundation guaranteeing access to instructive organizations, improvement in quality and pertinence of training
Mindfulness raising and mobilisation of families and networks against the misuse of kids
Social insurance projects and money transactions to improve the financial circumstances of families and to diminish the "need" to send kids to work
Coordinated activity is required between government divisions to battle the issue of youngster work.
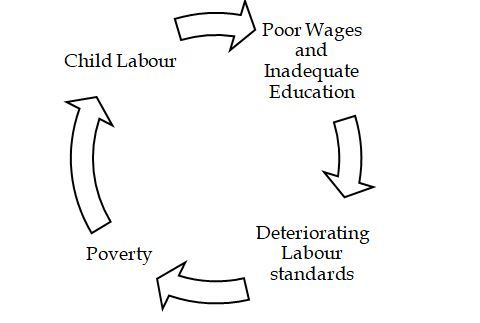
Child Labour And Economy Cycle Source: Forum IAS
Universal Safeguards
International Labor Organization (ILO) Conventions
The two Core Conventions straightforwardly identified with Child unjust Labour are that of ILO Convention 138 (Minimum age statute) and 182 (Worst types of Child Labor Convention). India has confirmed both the Core Conventions of the International Labor Organization (ILO) Conventions
Declaration of the Rights of Child, 1959 and Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 - stipulates (under article 25) that adolescence is qualified for extraordinary consideration and help. The above standards alongside different standards of all inclusive declaration concerning youngster were joined in the Declaration of the Rights of the Child, 1959.
United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child, 1989 It sets out various fundamental rights of kids cultural, political, monetary, social and wellbeing. Article 32 states that the administration ought to shield kids from work that is perilous or might hurt their wellbeing or their instruction.
Strategy Framework encompassing Child Labor:

Legal Frameworks Under Child Labour Source: Slide Share
Child Labor (Prohibition and Regulation) Act, 1986
In view of the suggestions of the Gurupadaswamy Committee (1979), the Act was passed in 1986. It has following targets:
to restrict the involvement of kids in specific occupations
furthermore, to manage the state of work of youngsters in certain different occupations.
Child Labor (Prohibition and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2016
The Amendment Act totally restricts the work of kids beneath 14 years.
The change additionally precludes the work of young people in the age gathering of 14 to 18 years in unsafe occupations and forms and manages their working conditions where they are not disallowed.
The alteration additionally gives stricter discipline to criminals for infringement of the Act and making the offense of utilizing any kid or juvenile in negation of the Act by a business as cognizable.
Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2000 and Amendment of the Act in 2006
It incorporates the working youngster in the classification of kids needing care and insurance, with no constraint of age or sort of occupation.
Segment 23 (brutality to Juvenile) and Section 26 (misuse of adolescent) explicitly manage kid work under kids needing care and assurance.
The Right to Free and Compulsory Education Act (2009): The Act made it required for the state to guarantee that all kids matured 6 to 14 years are in school and get free training.
Issues with Child Labor (Prohibition and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2016:
The rundown of unsafe ventures has been definitely diminished, this may permit the businesses in enterprises like synthetic blending units, cotton ranches, battery reusing units, and block ovens and so on to utilize pre-adult labour, which they may even get at an a lot less expensive cost.
Further, the correction enables youngsters to be utilized in "family or family enterprises".This brings up issue over an enormous number of kid work in agrarian country India where poor families are caught in intergenerational obligation- subjugation.
Definitional issue: One of the greatest difficulties in annihilating kid work is the perplexity around the meaning of a youngster, as far as age, in different laws managing kid work.
Absence of recognizable proof: Age ID of youngsters is a troublesome errand in India because of the absence of ID reports. Youngster workers frequently need school enrollment authentications and birth declarations, making a simple proviso in the law to abuse. Further, frequently offspring of displaced labours functioning as workers, those utilized in residential work regularly go unreported.
Powerless implementation of law and poor administration: Weak authorization of law, absence of robust discouragement and debasement is a noteworthy obstacle in destroying kid work

Say No to Child Labour Source: Opinion Front
Route Ahead:
Youngster work is an endless loop of neediness, joblessness, underemployment and low compensation. There ought to be purposeful exertion towards social insurance projects and money moves to improve the financial circumstances of families and to decrease the "need" to send kids to work
There is dire need to patch up instructive framework to guarantee access to instructive organizations, improvement in quality and pertinence of training
There is a need to bring consistency in existing Indian laws managing Child unjust Labour. The laws must extend the meaning of a kid by disallowing the work of and guaranteeing free and necessary training (RTE, Act, 2009) for youngsters underneath 18 years
There is a necessity to dispatch a national battle to conjure open intrigue and enormous scale cognition on exploitation of youngsters and the danger of Child unjust work.
Government should take sufficient measures to bring issues to light among families and networks. Parental proficiency can assume a significant job in guaranteeing the Fundamental rights of youngsters are maintained.
End of youngster unjust work requests responsibility from the general public for example family, state, common society and the individuals who utilize tykes in any undertakings
Numerous NGOs like Bachpan Bachao Andolan, ChildFund, CARE India, Talaash Association, Child Rights and You, Global walk against youngster work, RIDE India, Child line, Kailash Satyarthi Children Foundation and so forth have been attempting to kill kid labour in India.
