20 Weird Things You Didn't Know About Your Hair And Skin
Aug 06, 2019 • 7 views
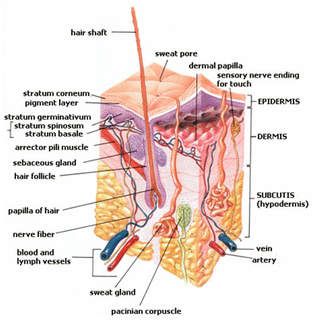
Hair is made up mostly ofkeratin, the same protein animals’ horns, hooves, claws, feathers, and beaks are made of.
When wet, a healthy strand oHair contains information about everything that has ever been in your bloodstream, including drugs, and is one of the most commonly used types of forensic evidence.f hair can stretch an additional 30% of its original length.
Hair grows slightly faster in warm weather, because heat stimulates circulation and encourages hair growth.
All hair is dead, with the exception of the hair that’s still inside the epidermis of your scalp.
The only thing about you that can’t be identified by your hair is your gender—men’s hair and women’s hair are identical in structure.
Black is the most common hair color.redis the rarest and only exists in about 1 percent of the world’s population, with blonde hair found in 2 percent.
As soon as a hair is plucked from its follicle, a new one begins togrow.
Hair is 50 percent carbon, 21 percentoxygen, 17 percentnitrogen, 6 percenthydrogen, and 5 percentsulphur.
Hair can grow anywhere on the human body with the exception of the palms of hands, soles of feet, eyelids, lips, and mucous membranes.
Goosebumps from cold or fear are the result of hair follicles contracting, causing the hair and surrounding skin to bunch up.
The average number of hair strands varies by natural color, with blondes having the most and redheads having the fewest.Aside from bone marrow, hair is the fastest growing tissue in the body.
The scientific term forsplit endsis “trichoptilosis.”
Balding only begins to become visible once you’ve lost over 50 percentof the hairs from your scalp.
A single hair has a lifespan of about five years.
Hair acts as a layer of thermally insulating protection for our heads, which lack the insulation that fat provides for the rest of our bodies.
Eightypercentof Americanswash their hairtwice a day.
Each strand of hair can support up to 100 grams in weight. Multiply that by the average 100,000 to 150,000 strands on each head, and your entire head of hair could support the weight equivalent to two elephants.

SKIN :
It's your body's largest organ, despite what the readers of Maxim think.
An average adult's skin spans 21 square feet, weighs nine pounds, and contains more than 11 miles of blood vessels.The skin releases as much as three gallons of sweat a day in hot weather. The areas that don't sweat are the nail bed, the margins of the lips, the tip of the penis, and the eardrums.
Ooh, that smell: Body odor comes from a second kind of sweat—a fatty secretion produced by the apocrine sweat glands, foFetuses don't develop fingerprints until three months' gestation.und mostly around the armpits, genitals, and anus.
Yum! The odor is caused by bacteria on the skin eating and digesting those fatty compounds.
Breasts are a modified form of the apocrine sweat gland.
Without a trace: Some people never develop fingerprints at all. Two rare genetic defects, known as Naegeli syndrome and dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis, can leave carriers without any identifying ridges on their skin
Fingerprints increase friction and help grip objects. New World monkeys have similar prints on the undersides of their tails, the better to grasp as they swing from branch to branch.
Blowin' in the wind: Globally, dead skin accounts for about a billion tons of dust in the atmosphere. Your skin sheds 50,000 cells every minute.
There are at least five types of receptors in the skin that respond to pain and to touch.
One experiment revealed that Meissner corpuscles—touch receptors that are concentrated in the fingertips and palms, lips and tongue, nipples, penis and clitoris—respond to a pressure of just 20 milligrams, the weight of a fly.
In blind people, the brain's visual cortex is rewired to respond to stimuli received through touch and hearing, so they literally "see" the world by touch and sound.
the buff" became synonymous for "nude" in 17th-century England. The term derives from soldiers' leather tunics, or "buffs," whose light brown color apparently resembled an Anglo-Saxon backside.
White skin appeared just 20,000 to 50,000 years ago, as dark-skinned humans migrated to colder climes and lost much of their melanin pigment.
I see very, very white people: Albinos are often cast as movie villains, as seen in The Da Vinci Code, Die Another Day, The Matrix Reloaded, and—inexplicably—the 2001 flick Josie and the Pussycats. Robert Lima of Penn State suggests that people associate pale-skinned albinos with vampires and other mythical creatures of the night.
More than 2,000 people have radio frequency identification chips, or RFID tags, inserted under their skin. The tags can provide access to medical information, log on to computers, or unlock car doors.
Flesh for fantasy: At the Baja Beach club in Barcelona, customers can get an implanted RFID "debit card" and party until their funds are exhausted.
The Cleveland Public Library, Harvard Law School, and Brown University all have books clad in skin stripped from executed criminals or from the poor.
Hopefully, they didn't have to reprint it: One such volume is Andreas Vesalius's pioneering 16th-century work of anatomy, De Humani Corporis Fabrica (On the Fabric of the Human Body).