Brain Drain
Apr 09, 2019 • 163 views
Definition :-
Human capital flight,more commonly known as " Brain Drain", is the large scale emigration of individuals with technical skills or knowledge.
Coined by the royal scociety to describe the emigration of "Scientists and technologists" to North America from post- war Europe.
Economic cost- Since emigrants take with them the fraction of value of their training sponsored by the govt or other organisations.
Causes:-
In terms of countries: Social envision,like health risks and lack of opportunities etc.
Individual reasons: Family influence,personal preference,seeking a better quality of life,higher paying jobs, etc.
History-
In 1963 the royal society coined this term
In 1972, the concept of 'reverse technological transfer" was developed by the UN conference on trades and development.
After the end of soviet union and warsaw treaty a huge brain drain started from the eastern european countries.

Negative effects:-
Loss of potential future entrepreneurs.
Shortage of important,skilled workers.
Loss of innovative ideas
Loss of critical health,education services.
Impact on rational identity.
Impact on integration and cohesion.
Positive effects:-
People moving to developed countries,learn new skills and expertise,which they can utilise to the advantage of the home economy once they return.
Remittances from abroad
Circulation of brains promotes integration to global markets.
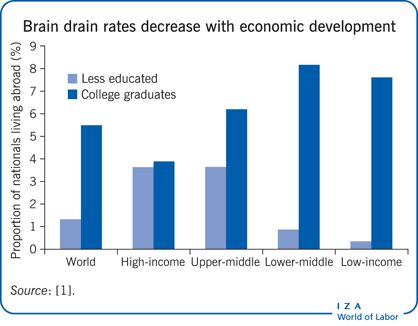
Limitations:-
Investment in higher education lost as emigrants becomes an asset.
Social capital associated with an individual is lost with departure.
Leaving of college graduates-
a) Whether their skills are put to good use in the destination country.
b) Shortage of skilled& competent people in native country.
Public sector- Pressure on govt. Budget argumentd pending pension,higher medical costs etc.
Human capital goes down and with that,the growth of technology too.
Solutions-
Improved educational system and promotion of people on merit alone.
Creating scope for scientific research
Generating funds for researches.
Providing attractive salaries to the highly qualified people.
BRAIN DRAN- BRAIN GAIN by monitoring the immigrating intellectuals and implementing ambitious recruiting programs.
Facts:-
India's million strong brain drain represents just 4.3 % of its vast graduate population.
In 2015,India had largest diaspore in the world at 16 million.
Countries facing massive brain drain- Ethiopia,South Africa,England,Malayasia, Iran , Mexico
