Skin Check For Cancer: Do Not Let It Ruin You................
Mar 27, 2019 • 865 views
Mutations occuring in the DNA of skin cells, cause the skin cancer.
The mutations tend the cells to grow out of control and formation of a mass of cancerous cells occurs.

Some warning signs of the skin cancer include:
1.
Any change observed in the size, colour, shape, or texture of a mole or other types of skin growth.
2.
Not healing of an open or inflamed skin.
3.
Telangiectasia:
A firm and transparent bump laced with the tiny blood vessels in thin red lines.
4.
Development of reddish or sometimes irritated patch of skin.
5.
Arriving of new and smooth skin bump called nodule with a raised border and indented center.
"Melanoma" is considered as the most dangerous type of skin cancer.
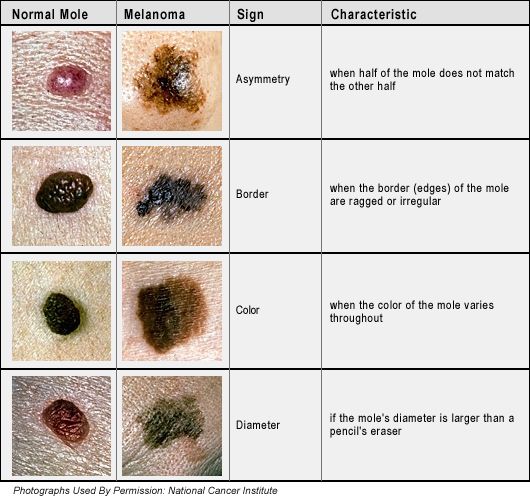
The signs of melanoma appear as:
1.
Any change in an existing mole.
2.
A small and dark spot in multicolour along with irregular borders .
They can be either elevated or flat which may bleed and then form a scab.
3.
Observing a cluster of shiny and firm bumps.
4.
Generation of a mole whose size is larger than a pencil eraser.
Diagnosis of the skin cancer:
Dermatologists use a dermatoscope (a special magnifying lens) to decide whether a skin lesion is harmless or not.
There is also a naked eye examination of the skin other than using a dermatoscope.
Dermatologist decides whether a biopsy is needed or not.
A biopsy can be conducted in a variety of different methods mentioned below.
Shave biopsy:
A shave biopsy is just like a test .
It is a very simple and common procedure. It can be performed by the dermatologists to see whether the skin lesion is really a skin cancer or not.
A small blade is used to take a small shaving of the upper layers of the skin under a local anaesthetic.
After that a dressing is applied to the wound that heals like a small graze.
The skin sample is then sent to the pathology lab for further assessment.
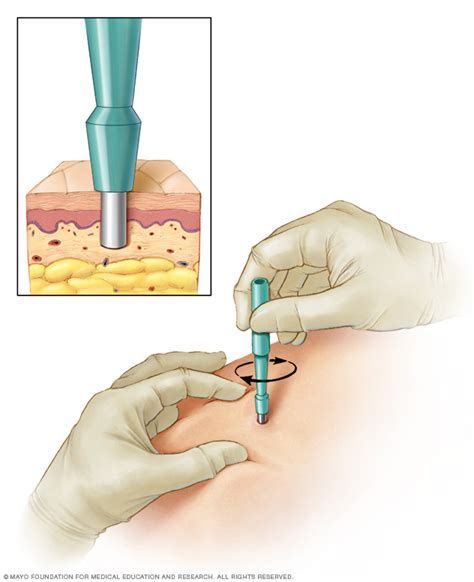
Punch biopsy:
A punch biopsy is also performed as a test.
It is a procedure performed by the dermatologists to see the skin lesion is really a skin cancer or not.
Under a local anaesthetic, a small pen-like device is used to core a small sample of the skin.
A stitch and dressing is then done after completion and can be removed in one to two weeks.
After that the skin sample is sent to the pathology lab for further assessment.
Excisional biopsy:
An excision biopsy is another diagnosis performed as a test.
It involves the cutting of a lesion out.
Under a local anaesthetic, the lesion is cut out in an oval shape and the wound is closed with stitches.
After that the skin sample is sent to the pathology lab for further assessment.
The treatment of skin cancer:
All the skin cancers cannot be treated in the same way.
Some of them need to be cut out completely .
Some can be scraped off or by frozen.
Some can be treated with creams or light or laser-based therapies.
Some of the skin cancers may require further treatments such as radiotherapy.
Liquid nitrogen (Cryotherapy):
This therapy can be used to treat several types of skin lesions.
Liquid nitrogen is applied either with a cotton wool or with a special spray gun.
The type of skin lesion that has, to be treated decides the intensity of the treatment.
The treatment can sting and cause some mild discomfort.
The area becomes red and swollen, within the first few hours and a blister can also develop.
The blister can be pierced with a sterile needle if it is tensed to allow the fluid to drain.
To speed up the healing process, various ointments are used .
In most cases, the area gets healed within two to three weeks.
A re-treatment is needed if the treated area does not clear up within four to six weeks. Skin biopsy can also be performed for confirmation.
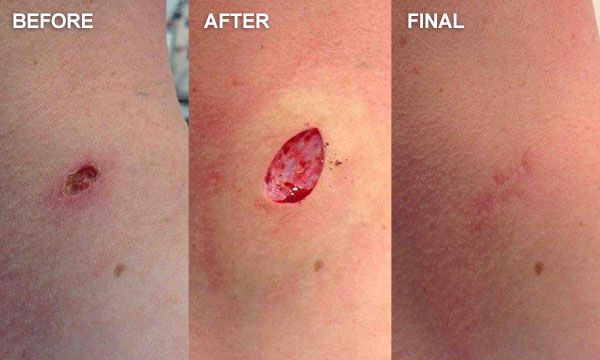
Excisional surgery:
Excisional surgery is one of the procedures commonly performed by the dermatologists to treat the initially generated cancerous skin.
The tumour is cut out in an oval shape so that it can be stitched up without the ends puckering , under the local anaesthetic.
The specimen is then sent to a pathology lab .
There it is looked at under a microscope by a pathologist.
The wound takes up to several weeks to heal up.
Photodynamic therapy and laser treatments
There is a specialised technique called photodynamic therapy which is used in the treatment of pre-cancerous lesions such as actinic keratoses and some early forms of skin cancer.
In this treatment the areas are lightly scraped followed by applying a specialised cream .
The cream get absorbed by the abnormal cells and get activated using either a special red light or laser light.
The treatment sessions that may be required can be one or two.
Some lasers are used to strip off the top layers of the skin for removing the precancerous lesions.
These treatments though work slowly but one should keep patience.
Special care should be taken and preventions should be followed.
Like wearing a protective clothing and including a wide-brimmed hat with sunglasses for UV protection.
Wearing a suncream and avoiding the unhealthy diets.
