You Are ‘Not’ What You Eat
Jul 11, 2019 • 15 views

ABOUT
Eating disorder is an illness that is characterized by over concern of body weight resulting into irregular eating habits. It is common in all ages, but people are more prone to it when they reach pre-adolescence or adolescence. In U.S. alone eating disorder affects millions of adolescents and young adults. Although it is treatable still if left unaddressed for a long time it can be deadly.
DATA
95% of those who suffer from eating disorder are between the ages of 12-25.
40-60% of elementary school girls are concerned about their weight and the concern endures through life.
In high school, 44% females and 15% males attempt to lose weight.
One half of teenage girls and one third of teenage boys use unhealthy weight control methods like smoking, skipping meals, purging, etc.
Westmead Hospital in Sydney and the Royal Children’s Hospital in Melboune have observed that eating disorder cases have increased in under -12 age group substantially.

CAUSES OF EATING DISORDERS
Although it is said that there is no actual root cause of eating disorder, still there is a general believe that eating disorders results from one or more biological, behavioral, and social factors including genetics, unpleasant experiences/trauma, peer pressure, teasing, family members with eating disorders, among others. There can be many biological factors resulting in eating disorder like irregular hormone function, genetics or nutritional deficiencies. Some psychological factors are negative body image and poor self-esteem. Environmental factors include dysfunctional family dynamic, professions like ballet and modeling, aesthetically oriented sports like rowing, diving, ballet, etc., family and childhood trauma, cultural or peer pressure.
TYPES OF EATING DISORDER
The most common forms of eating disorders are anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorder. It affects both males and females but it is seen to be more common in females than males.
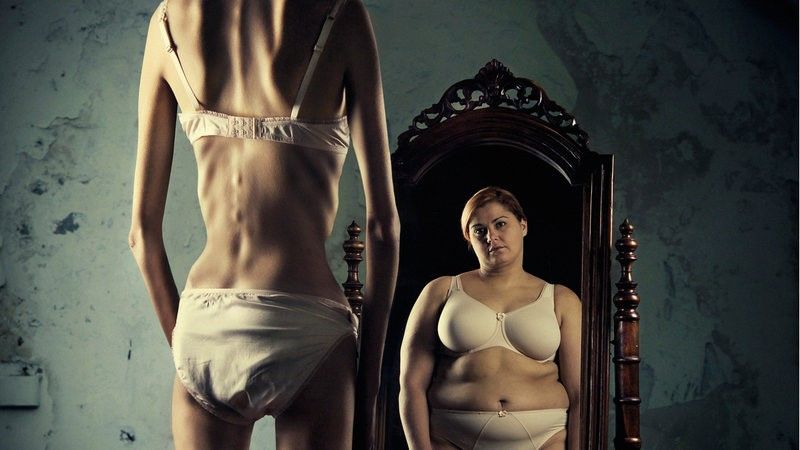
1-ANOREXIA NERVOSA: Here people avoid eating and control the quantity and quality of food they eat. Even if they are extremely thin and still feel fat, in a way they have obsessive fear of gaining weight. They typically diet too much because they have a very distorted image of their body. Physical signs of anorexia include excessive weight loss, weak, thinning hair, absence of menstrual cycle, etc. the risk of death is very high in these individuals.

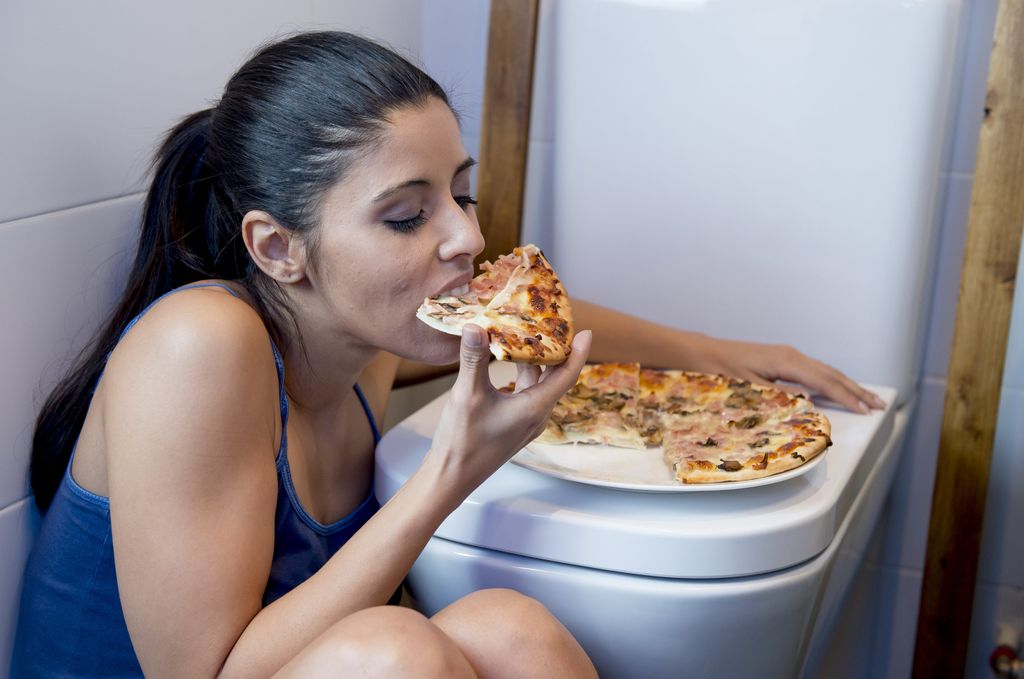
2- BULIMIA NERVOSA: teenagers with bulimia nervosa ‘binge and purge’. They have uncontrollable episodes where they overeat (bingeing) and then followed by using laxatives to purge. The repeated binge eating creates a feeling of shame and guilt that results in forceful purging. Physical signs of bulimia include discolored teeth, odor on breath, weakness or fatigue.

3-BINGE EATING: binge eating is somewhat similar to bulimia. The teenager loses control frequently and eats uncontrollably but is not followed by purging. People suffering from BED might be obese and it also increases risk of cardiovascular disease. Some signs of people suffering with binge eating are; eating rapidly, hiding food, discarding wrappers and containers, eating secretly, eating when depressed, feeling uncontrollable urge to eat, etc.

TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
As we know children learn a lot thorough imitating others. So parents, teachers and other elders should promote positive body image in young children. Other healthy relationships that elders can adopt are that they can avoid using food as bribes or punishments. Parents should accept the fact that all children have different eating habits from adults. Parents should not force diet on their child. Other habits include that parents should make children feel good about their body like not criticizing or teasing their children about their appearances.
Elders should encourage habit of sports and exercise for healthy body. A strong sense of identity and self-worth is important for children to help them develop coping strategies.
