Mri Scan: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Feb 12, 2019 • 18 views
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a fairly new technique that has been used since the beginning of the 1980
The MRI scanner uses magnetic and radio waves to create pictures of tissues, organs and other structures within the body, which can then be viewed on a computer.
This means that, unlike some other modes of medical imaging, there is no exposure to X-rays or any other damaging forms of radiation.
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is an imaging test that can give very detailed images of the inside of the body. Instead of using X-rays, MRI uses strong magnets, low-energy radio waves and a computer to produce images.
The pictures produced by an MRI scan, when compared to other imaging modalities, are much more detailed and therefore are of higher diagnostic quality when compared to more frequently used X-ray scanners
When is an MRI done?
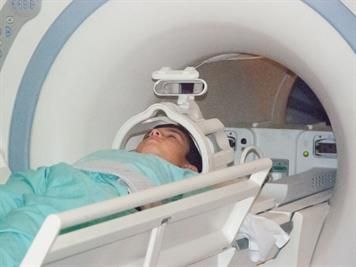
MRI is often recommended for imaging the brain and spine because of the detailed, high-quality images it provides. It is also useful in assessing knee injuries and other sports injuries as it is good at showing problems with soft tissues such as muscles, tendons and ligaments.
MRI is often used in addition to other tests, including other imaging tests such as ultrasound. MRI can sometimes show conditions or details that other imaging tests cannot provide.
How does an MRI work?
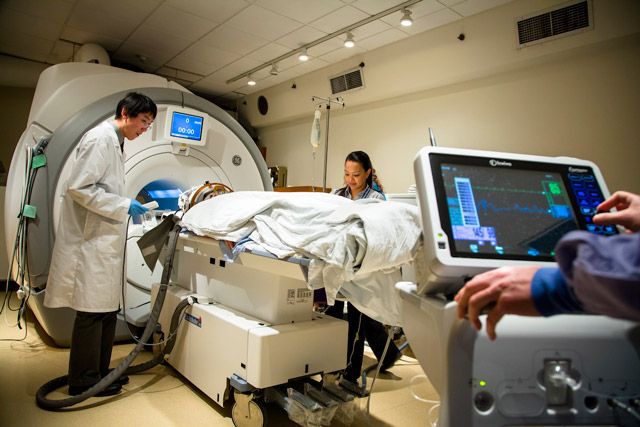
The strong magnets in the MRI scanner create a magnetic field, which causes the hydrogen atoms in your body to line up in the same direction. Radio waves are then passed into the part of your body being scanned, moving the hydrogen atoms out of alignment. When the radio waves are turned off, the atoms realign, and as they do so they produce radio signals. The signals are transmitted to radio antennae, or receivers, and the computer picks up this information and generates images.
Hydrogen atoms are found in water - H2O - and our bodies have a high composition of water, meaning hydrogen is found throughout the body. Because the hydrogen atoms in different types of body tissue realign at different speeds, they
produce different signals. Diseased tissue also gives off a different signal from healthy tissue. This allows the scanner to tell the difference between different tissue types and detect damaged or diseased tissue.
Things to be removed for mri scanning..
On the day of the test, wear loose, comfortable clothing that doesn't have snaps or other metal fasteners. You might need to take off your own clothes and wear a gown during the test.
Remove all of these before you go into the MRI room:
Cell phone
Coins
Dentures
Eyeglasses
Hearing aids
Keys
Underwire bra
Watch
Wig
metal clips on blood vessels in your brain;
a pacemaker or implanted defibrillator;
a surgically implanted joint/pin;
artificial heart valves;
a deep brain stimulator;
a cochlear implant;
magnetic dental implants;
drug infusion devices;
an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD);
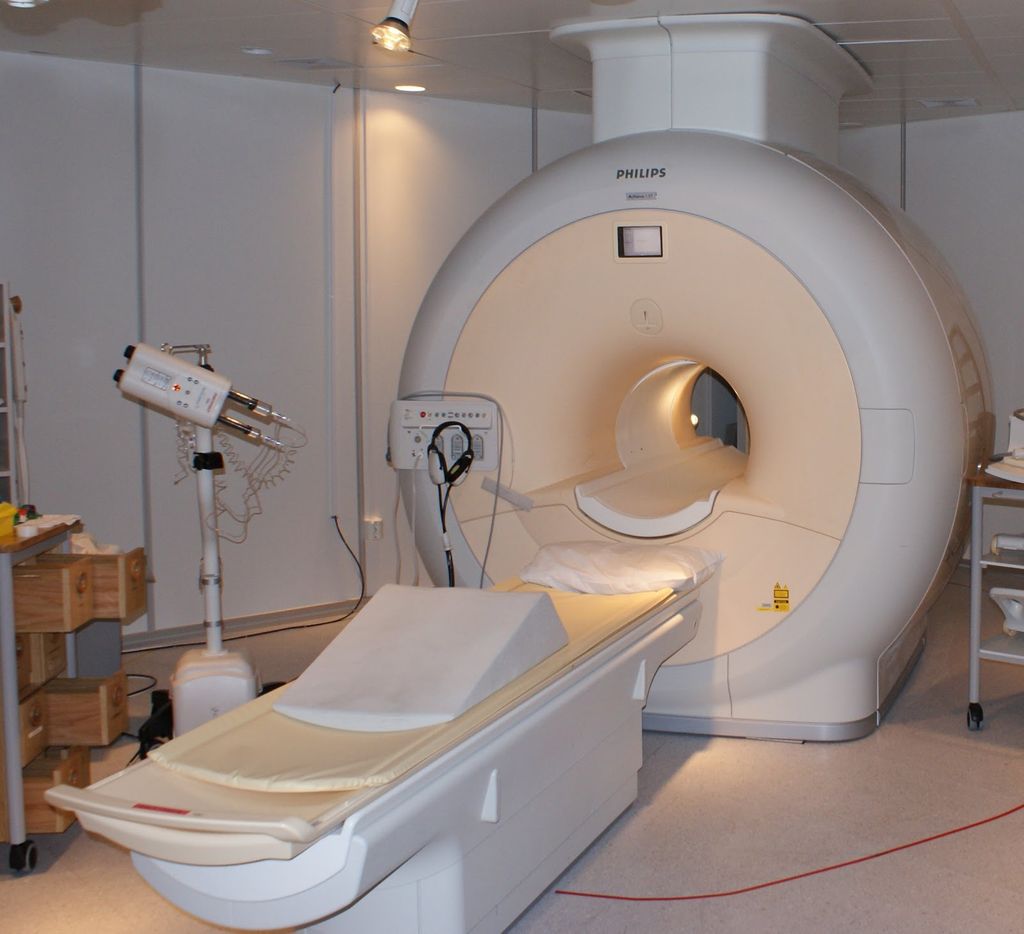
What Does the Equipment Look Like?
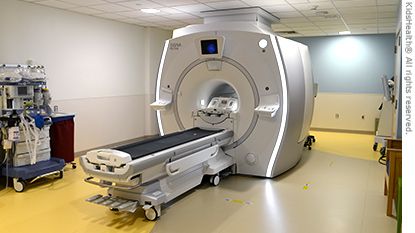
A typical MRI machine is a large tube with a hole at both ends. A magnet surrounds the tube. You lie on a table that slides all the way into the tube.
In a short-bore system, you are not totally inside the MRI machine. Only the part of your body that's being scanned is inside. The rest of your body is outside the machine.
An open MRI is open on all sides. This type of machine may be best if you have claustrophobia -- a fear of tight spaces -- or you're very overweight. The quality of images from some open MRI machines isn't as good as it is with a closed MRI.
