Classical Languages Of India
Jun 08, 2019 • 21 views

A classical language usually is a language with classical literature in its history. It is a prestigious, often an ancient language, such as Latin or Sanskrit. According to a linguist of the UC Berkeley College, George L. Hart, a Classical Language ought to be, ancient, an free, non-dependent tradition that rose mostly independently and freely, not as an subsidiary of another tradition and it must have a vast and a significantly rich body of ancient literature.
The word “classical” comes from the Latin word of “classicus”. The literary contributions of Rome and Ancient Greece in the Latin and Greek languages respectively were considered “classical” by academics and scholars.
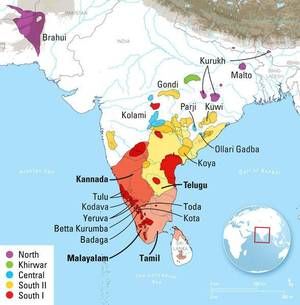
The first talks that which language should be awarded the status of a classical language in India was given to the language of Tamil by the Tamil academicians. The claim was that the Sangam Anthologies should be considered a classical form of literature. Its ancient prototypes were derived from the ancient Dravidian languages. The institution took a notice and then conferred the specialists of the Sahitya Academi.
Later a committee was set up and some standards were later established to grant the status of Classical Languages. The Criteria established for Classical Languages in India were as follow and the Government of India currently still follows the following criteria to gauge and determine if a language can be examined if they are fit to be classified as a “classical language”
1.Tall Archaic nature and high antiquity of its early writings/ recorded history over an interval of 1500-2000 years.
2.A massive body of ancient and archaic literature/ texts, which is deemed as valuable and important heritage by generations and generations of many researchers.
3.The classical language and its respective literature being different and quite distinct from the modernity of it, there may also be disjointedness between the classical language itself and the latter forms or its subsidiaries.
4.The literary tradition is and must be original and authentic and not borrowed or taken from another speech of community.
Tamil as mentioned above became the first Indian Classical Language. The government of India declared Tamil in 2004 as a classical language and later Sanskrit in 2005 as the second classical language.
These two languages are doubtlessly the benign sources for many languages belonging to the Dravidian family and Indo-European family of linguistic groups.
Later the government declared languages Kannada and Telugu (in 2008) as classical languages. In 2013, Malayalam was given the status of classical language as well. Odiya was given the status of the Classical language in the year 2014.
So, as of 2019, there are 6 classical languages of India.
