The Black Hole..
May 27, 2019 • 17 views
A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light cannot get out. The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying. Because no light can get out, people can't see black holes. They are invisible. The first modern solution of general relativity that would characterize a black hole was found by Karl Schwarzschild in 1916. On 10 April 2019, the first ever direct image of a black hole and its vicinity was published, following observations made by the Event Horizon Telescope in 2017 of the Super massive black hole.

Space telescopes with special tools can help in find black holes. The special tools can see how stars are very close to black holes and act differently than other stars. It is a great amount of matter packed into a very small area, think of a star ten times more massive than the Sun is squeezed into a sphere approximately the diameter of New York City. Even bigger black holes can result from stellar collisions. Soon after its launch in December 2004, NASA's Swift telescope observed the powerful, fleeting flashes of light known as gamma ray bursts. Chandra and NASA's Hubble Space Telescope later collected data from the event's "afterglow," and together the observations led astronomers to conclude that the powerful explosions can result when a black hole and a neutron star collide, producing another black hole.
Nature of the black hole
Super massive black holes, predicted by Einstein's general theory of relativity, can have masses equal to billions of suns; these cosmic monsters likely hide at the centers of most galaxies. The Milky Way hosts its own super massive black hole at its center known as Sagittarius, that is more than four million times as massive as our sun.
There are four types of black holes: stellar, intermediate, super massive, and miniature. The most commonly known way a black hole forms is by stellar death. As stars reach the ends of their lives, most will inflate, lose mass, and then cool to form white dwarfs. But the largest of these fiery bodies, those at least 10 to 20 times as massive as our own sun, are destined to become either super-dense neutron stars are called stellar-mass black holes.
Structure of simple black hole
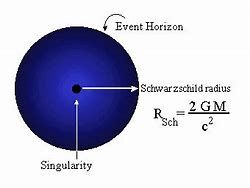
The characteristic of the structure of a black hole still remains one of the challenges of modern relativistic astrophysics. The Schwarzschild radius is the radius at which the escape velocity equals the speed of light. The surface of the sphere of radius equal to the Schwarzschild radius is called the event horizon. We on the outside of the black hole cannot learn anything about any event taking place within the event horizon, and thus we can think of it as the "surface" of the black hole. At the center of the black hole lies a singularity, that is, a region where the current laws of physics break down.
Could a black hole Destroy the Earth?
Black holes do not go around in space eating stars, moons and planets. Earth will not fall into a black hole because no black hole is close enough to the solar system for Earth to do that. Even if a black hole the same mass as the sun were to take the place of the sun, Earth still would not fall in. The black hole would have the same gravity as the sun. Earth and the other planets would orbit the black hole as they orbit the sun now.The sun will never turn into a black hole. The sun is not a big enough star to make a black hole. A Black hole holds all the colors of the universe.
