Unraveling A Mystery Of Space, The Black Holes
Mar 31, 2019 • 35 views
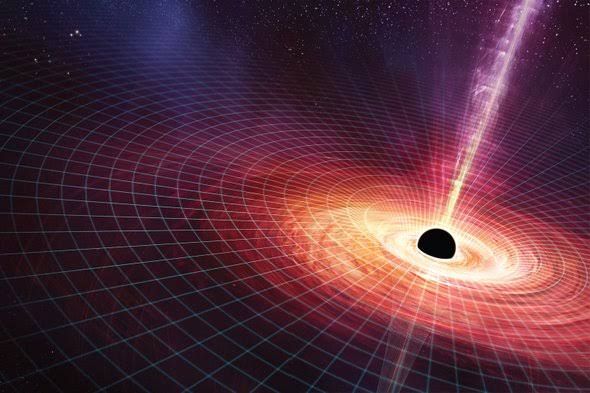
Black holes are no exception to the complexities and enigma of space. The name itself may sound suspicious to us, but as theories are concerned, a black hole is a massive amount of mass concentrated into a very small area – think of the mass of a star which is more massive than our sun is concentrated in an infinitely dense point. Black hole alike an invisible corpse of a dead star. Einstein’s theory of general relativity shows us that when a massive star dies, a very small and dense core is left behind. Its gravity is so intense that nothing moving near its invisible border can escape. The new pictures of several black holes are fascinating the astronomers to explore more about this strange thing.Astronomers are able to see or detect black holes but they can study its behavior when it undergoes a process called accretion, where a black hole pulls a matter inside when it is passing by an interstellar cloud. Even if it is a massive star, the black hole would tear the star apart while the process of accretion is carried out.
Formation of black holes
In final stages of the stars, they burn out with massive cosmic explosions known as supernovae. The core of the dying star is left behind and other star matters are spread out in space in the process. Gradually the core starts to collapse in on itself due to the instability of balancing forces. Here a black hole is formed if the mass gets collapsed into an infinitely small point. This concentration of all the mass into such a tiny point gives the black hole enormous gravitational pull.
Size of Black holes:
Black holes are either smaller or massive in size range. Recently, black holes of intermediate size have also been found. Smaller black holes are often called “stellar” with a mass of 10 to 20 times as massive as the sun. The biggest sized black holes are called supermassive black holes with 1 million times as massive as the sun.Astronomers have found that at the center of every galaxy there lies a supermassive black hole. Sagittarius A, the supermassive black hole at the center ofmilky way galaxy is about 4 million times as massive as the sun that can fit millions of earth inside of it.
How to detect black holes :
As even the light can’t pass out of the black hole, it’s totally invisible and obviously strange! It can only be detected by its behavior and effects on the neighbors aroundas it pulls inside everything that comes near its invisible edge. Study of stars can be used to detect whether a black hole is around. During the process of engulfing a celestial object by the black holes, a high energy light is radiated followed by gamma-ray bursts which are known to most energetic and brightest in the universe.
