WHAT IS MARKETING?
In easy words we can say, marketing is a business process of creating relationships with customers and satisfying them.The 'marketing concept' proposes that in order to follow the organizational objectives, an organization should analyse the needs and wants of potential consumers and satisfy them more effectively than its competitors, and for that we have to know what is need and want of the customers:-
1.Needs:Something necessary for people to live a healthy, stable and safe life. When needs remain unfulfilled, there is a clear adverse outcome: a dysfunction or death. Needs can be objective and physical, such as the need for food, water, and shelter; or subjective and psychological, such as the need to belong to a family or social group and the need for self-esteem.
2.Wants:Something that is desired, wished for. Wants are not essential for basic survival and are often shaped by culture or peer-groups.
3.Demands:When needs and wants are backedby the ability to pay, they have the potential to become economic demands.
Now as we get to know what is marketing, the question arises that on what basis we will sell our products to customers and this can be found in marketing mix. Marketing mix is based upon four controllable variables that a company manages in its effort to satisfy the corporation's objectives as well as the needs and wants of atarget market. These are as follows:-
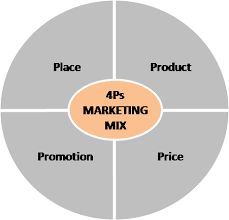
·Product
The product aspects of marketing deal with the specifications of the actual goods or services, and how it relates to theend-user's needs and wants.
·Pricing
This refers to the process of setting apricefor a product, including discounts. The price need not be monetary; it can simply be what is exchanged for the product or services, e.g. time, energy, or attention or any sacrifices consumers make in order to acquire a product or service.
·Place (ordistribution)
This refers to how the product gets to the customer; the distribution channels and intermediaries such as wholesalers andretailerswho enable customers to access products or services in a convenient manner.
·Promotion
This includes all aspects of marketing communications;advertising,sales promotion, includingpromotional education,public relations,personal selling,product placement,branded entertainment, event marketing, trade shows andexhibitions. This fourth P is focused on providing a message to get a response from consumers that is designed to persuade or tell a story to create awareness.
Communication

Marketing communicationsis an audience-centered activity designed to engage audiences and promote responses. It is defined by actions a firm takes to communicate with end-users, consumers, and external parties.
Marketing communications encompass four distinct subsets, which are:
Personal sales
Oral presentation given by a salesperson who approaches individuals or a group of potential customers:
·Live, interactive relationship
·Personal interest
·Attention and response
·Interesting presentation
·Clear and thorough.
Sales promotion
Short-term incentives to encourage buying of products:
·Instant appeal
·Anxiety to sell
An example is coupons or a sale. People are given an incentive to buy, but this does not build customer loyalty or encourage future repeat buys. A major drawback of sales promotion is that it is easily copied by competition. It cannot be used as a sustainable source of differentiation.
Public relations
Public relations(or PR, as an acronym) is the use of media tools in order to promote goodwill from a business or organization to a target market segment, or other consumers of a firm's good/service. PR stems from the fact that a firm cannot seek to antagonize or inflame its market base, due to incurring a lessened demand for its good/service. Organizations undertake PR in order to assure consumers, and to forestall negative perceptions towards it.
PR can span:
·Interviews
·Speeches/Presentations
·Content
·Corporate literature, such as financial statements, brochures, etc.
Publicity
Publicity involves attaining space in media, without having to pay directly for such coverage. As an example, an organization may have the launch of a new product covered by a newspaper or TV news segment. This benefits the firm in question since it is making consumers aware of its product, without necessarily paying a newspaper or television station to cover the event.
Advertising
Advertisingoccurs when a firm directly pays a media channel to publicize its product. Common examples of this include TV and radio adverts, billboards, branding, sponsorship, etc.
Mix
Marketing communications mix is used to reach, engage, and provoke audience-centered conversations. It consists of 5 tools, which are 1) Advertising, 2) Sales & Promotion, 3) Public Relations, 4) Direct Marketing and 5) Personal Selling. The types of messages that are enhanced can be 1) Informational, 2) Emotional, 3) User-generated, or/and 4) Brand content. The last main component of MC Mix is Media, which corresponds to the channel used to send the message. Media is divided into 3 categories, and these are media by 1) Form, 2) Source and 3) Functionality.
