Nuclear Technology
Jun 23, 2019 • 9 views
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions that release nuclear energy to generate heat which most frequently is then used in steam turbines to produce electricity in a nuclear power plant. As a nuclear technology, nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions.
Why nuclear power
Nuclear power is a clean and efficient way of boiling water to make steam, which turns turbines to produce electricity. Except for the reactor, nuclear power stations work like most coal or gas-fired power stations. Nuclear power offers many benefits for the environment as well.
When it comes to efficiency and reliability, no other electricity source can match nuclear. Nuclear power plants can continuously generate large-scale, around-the-clock electricity for many months at a time, without interruption.
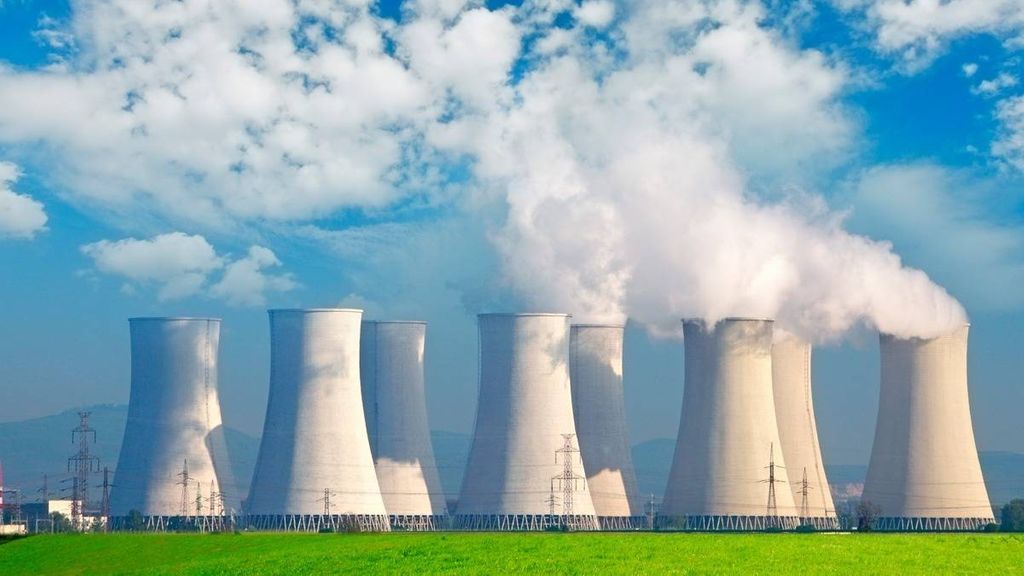

How is nuclear power generated
Nuclear power plants use low-enriched uranium fuel to produce electricity through a process called fission—the splitting of uranium atoms in a nuclear reactor. Uranium fuel consists of small, hard ceramic pellets that are packaged into long, vertical tubes. Bundles of this fuel are inserted into the reactor.
A single uranium pellet, slightly larger than a pencil eraser, contains the same energy as a ton of coal, 3 barrels of oil, or 17,000 cubic feet of natural gas. Each uranium fuel pellet provides up to five years of heat for power generation. And because uranium is one of the most abundant metals, it can provide fuel for the world’s commercial nuclear plants for generations to come.
Disadvantages
Huge amount of radioactive waste is produced which is extremely dangerous.
During the operation of Nuclear power plants, radioactive waste can also be used for production of nuclear weapons.
Uranium, an important source for nuclear reactions, is a scarce source on earth.
Advantages
Nuclear power generation emits relatively less amount of carbondioxide(CO2).
It is possible to generate high amount of electricity at a single plant.
This technology is readily available, it does not have to be developed first.
Uses of nuclear technology in addition with nuclear power
There are a number of other beneficial uses for nuclear technology in addition to creating electricity. These range from agriculture to medical, and space exploration to water desalination.
Agriculture and Food
In many parts of the world, agricultural workers use radiation to prevent harmful insects from reproducing. When insects cannot have offspring, there are fewer of them. Reducing the numbers of pests and bugs protects crops, providing the world with more food.
Medical
Nuclear technologies provide images inside the human body and can help to treat disease. Hospitals sterilize medical equipment with gamma rays safely and inexpensively. Items sterilized by radiation include syringes, burn dressings, surgical gloves and heart valves.
Space Exploration
Nuclear technology makes deep space exploration possible. The generators in unmanned spacecraft use the heat from plutonium to generate electricity and can operate unattended for years. This reliable, long-term source of electricity powers these spacecraft, even as they venture deep into space.
Water Desalination
Water desalination is the process of removing salt from saltwater to make the water drinkable. However, this process requires a lot of energy. Nuclear energy facilities can provide the large amount of energy that desalination plants need to provide fresh drinking water.
