All You Need To Know About Gravity
Jun 17, 2019 • 14 views
Gravity is the force of attraction that pulls things together. On Earth, we experience it as the force that pulls us down onto the surface of the planet. In the Universe, gravity is the force that pulls planets in orbit around stars.
Gravity may seem impressive, but it is actually the weakest known force in the Universe. It takes objects the size of planets and stars to produce a noticeable effect. The Sun's gravity is strong enough to hold all the planets of the solar system in orbit around it. Take up skydiving and you will soon feel the full effects of gravity at work. When you jump out of a plane, gravity makes your body accelerate towards the ground. At the same time, air rubs against your body, creating friction, or drag, which work against gravity. Eventually the two forces balance, and you stop accelerating- you have reached "terminal velocity".
Gravity and scienitists
Galileo
The first scientist to study gravity seriously was an Italian ccalled Galileo Galilei. He did lots of experiments and concluded that in the absence of air resistance all falling objects would accelerate dowward at the same rate. It is the air resistance, called drag, that allows some objects to reach the ground more slowly than others. According to legend, Galileo dropped balls of different weight from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to show they hit the ground at the same time.
Newton
Sir Issac Newton was the first person to figure out that the force of gravity keeps the Moon trapped in orbit around the Earth. Legend has it that Newton came up with his theories about gravity when he saw an apple fall from a tree. He howed that the force that pulled the apple to the ground was the same force that pulled the Moon into Earth orbit.
Einstein
Relative success:Einstein came up with his theory in 1916. A few years later, astronomers shown he was right, when light from a distant star was shown to bend as it passed the Sun.
Warp factor: Albert Einstein came up with another theory to explain gravity. He suggested that a big mass, such as a planet, warps space and time in the same way as a heavy ball resting on a rubber sheet.
Centre of gravity: Gravity pulls down on an object through a point called the centre of gravit. An object will tip over if the centre of gravity is too high or moves outside the base of the object. All- terrain vehicles have a very low centre of gravity so they can drive up an down steep slopes.
Exploding Stars: Stars are powered by nuclear reactions. In the core of the Sun, hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing extreme heat. When the Sun runs out of hydrogen in its core, the core will collapse. The collapse of the core of a larger star might release enouh energy that the star is seen as a supernova. The outer parts of the star are blown into space.
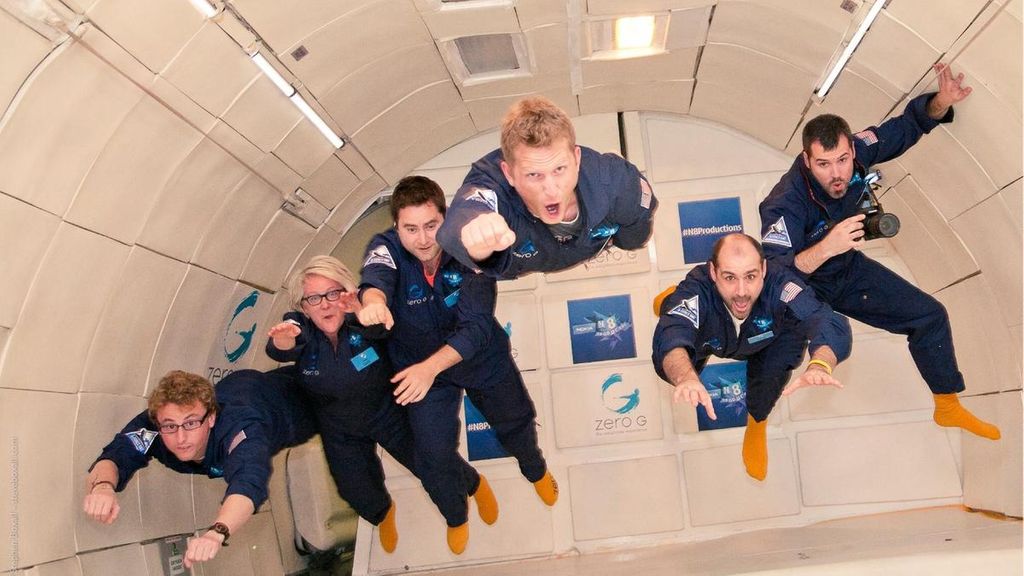

Zero gravity: It is not necessary for you to travel to space to know how zero gravity feels like. Some places and ways where you can get an experience of zero gravity are – roller coaster rides, riding a plane, diving underwater, free falling, etc. An excellent example of experiencing zero gravity is the Vomit Comet.
The vomit comet is an aircraft designed to provide a zero gravity experience to the astronauts. It dives and rises so as to create brief spells of zero gravity inside the aircraft. In fact, the astronauts and the aircraft are accelerating at the same rate, but there is no contact betwwn them.
