Additive Printing
Jun 19, 2019 • 10 views
3D printing is an innovative technology that lets you create a physical object from a digital model. It started in the 80's under the name of rapid prototyping because the purpose of this technoloy is to prototype faster and cheaper. The term 3D printing covers a variety of processes in which material is joined or solidified under computer control to create a 3-Dimensional object, with material being added together, typically layer by layer. A lot's changed since then, and today 3D printers offer amazing results and let you create anything you can imagine!
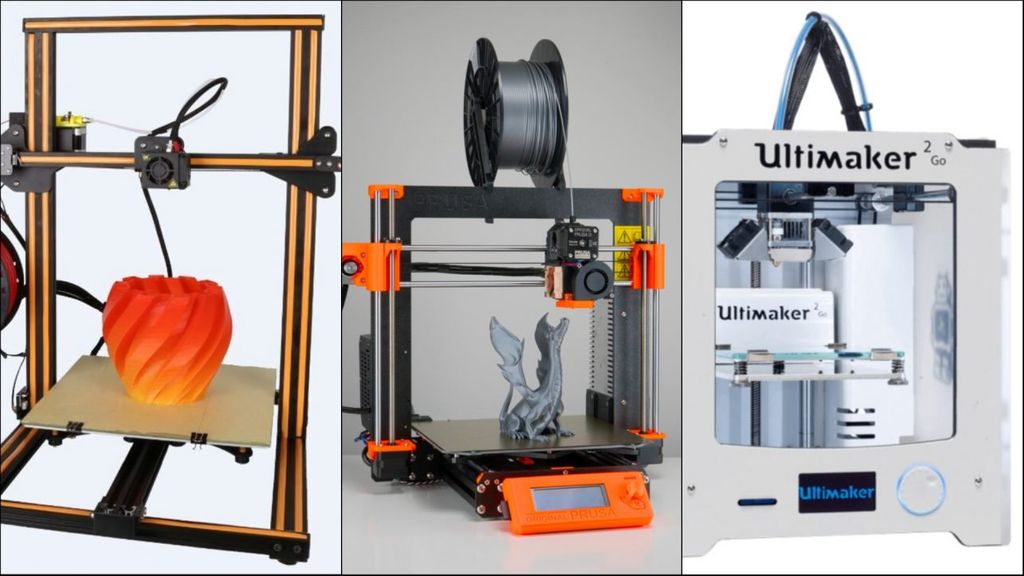

How it works
3D printing is also called additive manufacturing, because unlike the traditional subtractive manufacturing, 3D printing does not remove material, it adds it, layer by layrer. In order to print something, first you will need a 3D model of the object you want to create, which you can design in a 3D modeling proram like CAD- Computer Aided Design.
Just like a document printer requires a document or PDF for printing, 3D printers require digital design files of 3D objects.
Once you have the digital design saved, your computer will process the file and get ready for printing. You can change settings just like you change settings in a normal printer.
Next, you choose a material(like plastic) and load the 3D printer with enough material. In a 3D printer we use different filaments made of different materials.
A 3D printer creates a physical object by depositing many layers of materials on a print bed. When your 3D printer is loaded with materials, the computer will now send instructions to the 3D printer about how to deposit the material layer by layer to recreate a physical copy of the digital design.
Advantages of 3D printing
Speed
One of the main advantages of additive manufacture is the speed at which parts can be produced compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Complex designs can be uploaded from a CAD model and printed in a few hours. The advantage of this is the rapid verification and development of design ideas.
Single step maufacture
Additive manufacturing machines complete a build in one step, with no interaction from the machine operator during the build phase. As soon as the CAD design is finalized, it can be uploaded to the machine and printed in one step in a couple of hours.
Cost
One of the main advantages of 3D printing is the the low cost of labor. Moreover, the ability to produce complex geometries in a single step results in higher efficiency and turn around. Machine operation costs are typically the lowest contributor to the overall cost of manufacture.
Risk mitigation
Being able to verify a design by printing a production-ready prototype before investing in expensive manufacturing equipment (e.g. molds or tooling and jigs) eliminates the risk during the prototyping process.
Complexity and design freedom
Since components are constructed one layer at a time, design requirements such as draft angles, undercuts and tool access do not apply, when designing parts to be 3D printed. This gives designers a large amount of design freedom and enables the easy creation of very complex geometries.
Sustainibility
Additive manufacturing methods generally only use the material needed to build a part. Most processes use raw materials that can be recycled and re-used in more than one builds. As a result, additive manufacturing process produces very little waste.
Normal 3D printer can only print plastic like materials but not able to print metal 3D objects. To overcome this, 3D metal printing came into the scenario.
3D Metal printing
3D printing, in contrast, uses almost precisely as much material as is present in the actual object, bringing wastage down to nothing whatsoever. But all this didn’t count until now, because of the huge limiting factor that 3D printers could only work in plastic. But now, several companies across the world are designing 3D printers that print in metal instead of plastic.
Metal printing is a relatively new technique based on an existing technology. It has proved to be invaluable in the prototyping process, but its high cost is the factor that prevents it from being used widely. Other limiting factors include the relative lack of accuracy on the small scale, and high cost of parts. We can expect, however, that this will be gradually resolved as technology advances. In conclusion, this is a good thing that’s worth waiting for!
