Tcp/Ip Reference Model
May 05, 2019 • 132 views
The TCP/IP reference model was developed prior to OSI model. The major design goals of this model were,
1. To connect multiple networks together so that they appear as a single network.
2. To survive after partial subnet hardware failures.
3. To provide a flexible architecture.
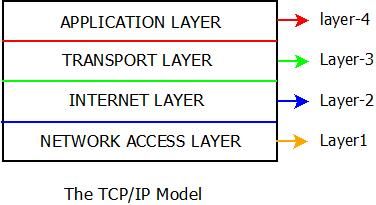
Unlike OSI reference model, TCP/IP reference model has only 4 layers. They are,
1. Host-to-Network Layer
2. Internet Layer
3. Transport Layer
4. Application Layer
Layer 1: Host-to-network Layer
1. Lowest layer of the all.
2. Protocol is used to connect to the host, so that the packets can be sent over it.
3. Varies from host to host and network to network.
Layer 2: Internet layer
1. Selection of a packet switching network which is based on a connectionless internetwork layer is called a internet layer.
2. It is the layer which holds the whole architecture together.
3. It helps the packet to travel independently to the destination.
4. Order in which packets are received is different from the way they are sent.
5. IP (Internet Protocol) is used in this layer.
6. The various functions performed by the Internet Layer are: o Delivering IP packets o Performing routing o Avoiding congestion
Layer 3: Transport Layer
1. It decides if data transmission should be on parallel path or single path.
2. Functions such as multiplexing, segmenting or splitting on the data is done by transport layer.
3. The applications can read and write to the transport layer.
4. Transport layer adds header information to the data.
5. Transport layer breaks the message (data) into small units so that they are handled more efficiently by the network layer.
6. Transport layer also arrange the packets to be sent, in sequence.
Layer 4: Application Layer
The TCP/IP specifications described a lot of applications that were at the top of the protocol stack. Some of them were TELNET, FTP, SMTP, DNS etc.
1. TELNET is a two-way communication protocol which allows connecting to a remote machine and run applications on it.
2. FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a protocol, that allows File transfer amongst computer users connected over a network. It is reliable, simple and efficient.
3. SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol) is a protocol, which is used to transport electronic mail between a source and destination, directed via a route.
4. DNS (Domain Name Server) resolves an IP address into a textual address for Hosts connected over a network.
5. It allows peer entities to carry conversation.
6. It defines two end-to-end protocols: TCP and UDP
o TCP (Transmission Control Protocol):
It is a reliable connection-oriented protocol which handles byte-stream from source to destination without error and flow control.
o UDP (User-Datagram Protocol):
It is an unreliable connection-less protocol that does not want TCPs, sequencing and flow control. Example: One-shot request-reply kind of service.
Merits of TCP/IP model
1. It operated independently.
2. It is scalable.
3. Client/server architecture.
4. Supports number of routing protocols.
5. Can be used to establish a connection between two computers.
Demerits of TCP/IP
1. In this, the transport layer does not guarantee delivery of packets.
2. The model cannot be used in any other application.
3. Replacing protocol is not easy.
4. It has not clearly separated its services, interfaces and protocols.
