Twin Study By Nasa - Game Changer For Future Astronauts
Apr 28, 2019 • 360 views
NASA astronaut Scott Kelly spent almost one year orbiting Earth aboard the international space station. He has an identical twin who is also an astronaut. Mark and Scott Kelly were the central figures of a totally new unique twin study. This helped us learn what happens to our bodies during long term spaceflight.
NASA came up with this concept so it would be incredibly useful in the future to do a research project and study the effects of long term space flight on not only physiological parameters which has already been done for decades now but mainly on molecular information using Mark as a reference because he is genetically identical.
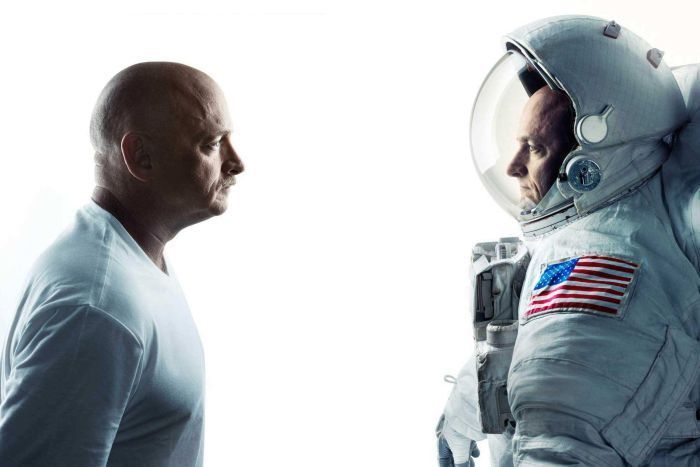
This was done by Scott Kelly collecting biological samples like blood and urine while in space and at the same time, the exact same type of samples was called from his twin brother Mark and it was compared. Both twins were monitored closely before, throughout and after the mission creating a massive amount of data. Now the data obtained is classified into 3 categories: Low risk, medium risk and high risk.
Examples for the ones that don’t seem to pose a significant risk are body mass decrease, inflammation increase but mostly temporarily. Medium risk stuff is usually about interruption in the collagen regulation (Collagen synthesis is a complex orchestration of intracellular and extracellular events). This could result in blood pooling at the bottom of our legs or issues with blood pressure regulation. And now for the high risk stuff. After a comprehensive computerized tests were conducted on Scott Kelly, it was apparent that cognitive functions like emotion recognition and abstract matching accuracy declined during spaceflight. These declines lasted about 6 months after returning to Earth.

Another major concern is thickening of vascular walls, increase in vascular stiffness and a ballooning effect in the vasculature of the upper body. Scientists are still unsure if this can be cured over time when the astronauts return to earth. Overall, the experiment was successful is giving insight into the potential molecular mechanisms which could be effected by spaceflight. Considering that many space organizations such as NASA are planning for long spaceflights in the future such as a manned mission to Mars, such study could probably be the most essential when it comes to saving the astronauts life.
