Concept Of Price Line In An Economy
Jun 06, 2019 • 25 views
Price or budget line tells the various possibilities of combination of goods that can be bought by a complete usage of a particular amount of income. Its relevance is simple, it tells the optimum usage of certain amount of money or in economic terms, it states optimum usage of one's income.
In miniscule level or Microeconomics, the study of a budget line is restrained to showing the fluctuation over two goods only to simplify studies. For example, a consumer has weekly income of 600 rupees. He purchases only two goods, packets of biscuits and packets of coffee. The price of each packet of biscuits is 60 rupees and the price of each packet of coffee is 120 rupees . Given the assumed income and the price, of the two goods, the consumer can purchase various combination of goods or market combination of goods weekly.
A graphical representation of the above case would be as follows:
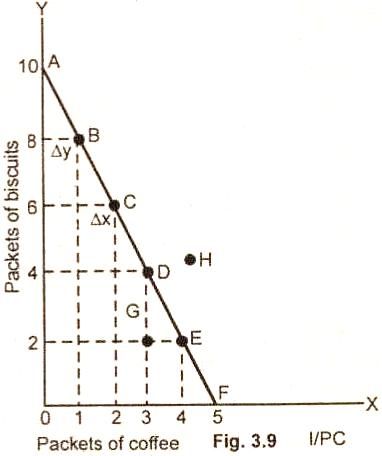
Line AF would be the budget or price line representing the various combinations of biscuits and coffee that can be bought with the assumed prices and fixed income.
This study is very simple and helps in understanding consumer equilibrium. But, what is it's relevance in Macroeconomics? What is the concept of price line in an economy?
In macroeconomics, the relevance of budget line is in understanding the consumer's behaviour, inclinations and most importantly its affordability towards a combination of goods. The study of this arena helps the producers in deciding the various aspects of a product before it is launched in the market i.e. quality on the criteria of setting it's price which in turn dependant on the affordability of the consumer house in general. In nutshell, it helps in understanding the demand of the product in the market on the grounds of its price alone by understanding the affordability of the consumer.
The indifference curve analysis helps in comparing various budget or price lines and helps in understanding the impact of various factors on consumer's behaviour. A higher indifference curve indicates higher level of consumer's satisfaction and vice-versa.
The utility of a good or service to the consumer is key to stating its price line. Microeconomists have stated various approaches i.e. qualitative and quantitative approaches to determine its value for a commodity.
The key concepts of Microeconomics are conventional and rigid in nature. Their relevance in understanding and foreseeing the modern economy 's behaviour is miniscule. What it states is fundamental to outlaying the structure of the economy and making it's core understanding.
The fundamental consumer theory simply outlines a generic consumer behaviour based on a lot of assumptions making it unreliable in predicting the consumer's response on a macro level yet it holds significant relevance as it formulates the utility and consumer behaviour.
