Financial Decisions
Aug 26, 2019 • 86 views
Financing decisions are one of the most crucial decisions taken by the finance manager of a company. Financing decisions majorly revolve around the capital structure i.e funds borrowed and allocated by an organization for the purpose of investment.
A finance manager has numerous responsibilities while deciding the financial matters of an organization –
• Budget and budgetary control
• Preparation of financial statements
• Accounting as per applicable financial reporting framework
• Meeting legal requirements
• Profit maximization
1. Company profit maximization
2. Shareholder's wealth maximization
• Financing decisions
Debt to Equity ratio
An appropriate financing decision would involve an exactly favorable ratio of debt to equity.It is risky for a business to indulge in high debt/equity ratios.
If a lot of debt is used to finance growth, a company could potentially generate more earnings than it would have without that financing. Share value or share earnings increase when leverage earnings are higher than interest/debt costs. However, if the cost of debt financing outweighs the increased income generated, share values may decline. The cost of debt fluctuates regularly along with market conditions. At the initial stages, unprofitable ratios are not recommended.
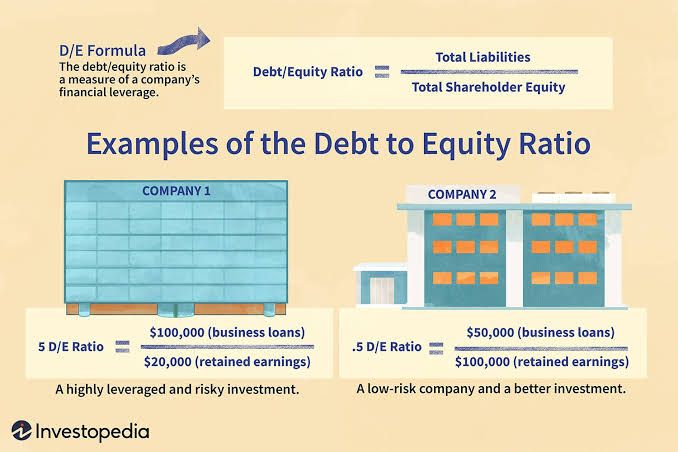
Debt to equity examples ; Source - Investopedia.com
Various factors that affect the financing decisions:
1. Cost of funds – Each source of funds comes with a measurable cost. The most appropriate way to determine the correct cost of debt or equity is to include its growth factor.
A)Cost of debt- Cost of debt is the amount paid as interests on all its debts divided by the total debts. It is very important to include the tax factor to accurately measure the cost.
Cost of Debt = Interest Expense (1 – Tax Rate)
B) Cost of Equity – Equity costs are the amounts paid to the equity shareholders as a compensation paid to them, for the risk undertaken by them, by investing capital in the firm.
Cost of equity for a company paying dividends with an assumed growth - Re = (D1 / P0) + g
There are several methods to calculate Cost of Equity. Each method is applicable as per the market situations and their controlling factors. To know more about Cost of Equity click here.
C) Cost of retained earnings- Cost of retained earnings is the same as Cost of Equity after including the growth factor.
This cost determines the opportunity cost of the funds that the shareholders forego by re-investing their funds in the firm.
D) Floatation costs- Each source of funds comes with a cost to generate it. This cost is separate from the cost paid as interests or dividends. For eg: Brokerage costs, Securities Transaction Tax (STT)
2. Risk – Every mix in capital structure outline comes with significant risks. If a firm opts for high debt, there is a potential loss of income by paying high rates of interest. For a few companies, this could be a driver of bankruptcy.
However, this doesn’t imply that the business shall simply opt for more equity in their capital structure. High equity leads to loss of ownership.
3. Control – Debt and Equity both come with different control risks. High equity could hinder decision making processes and High debt may induce creditors to interfere in investment decisions in order to protect their money in the firm.
4. Cash flow – Every company should have a detailed understanding of their cash generating operations. Unpaid debt interests may lead a company to lose more of its share value too.
Cash flow statement elements ; Source - edupristine.com
An optimal capital structure should take the company's current and estimated future cash flows in consideration.
5. Economic market conditions –
• Economic prosperity or market depression.
• Government policies (trade regulations)
• Taxation policies
To know more about economic factors that affect the financial decisions, click here.
Earnings
One of the primary objectives of a company is to maximize shareholders wealth. Shareholders gain profits of the company through dividends. A practical understanding of Earnings Per Share (EPS) explains how different debt and equity ratios affect the shareholders.
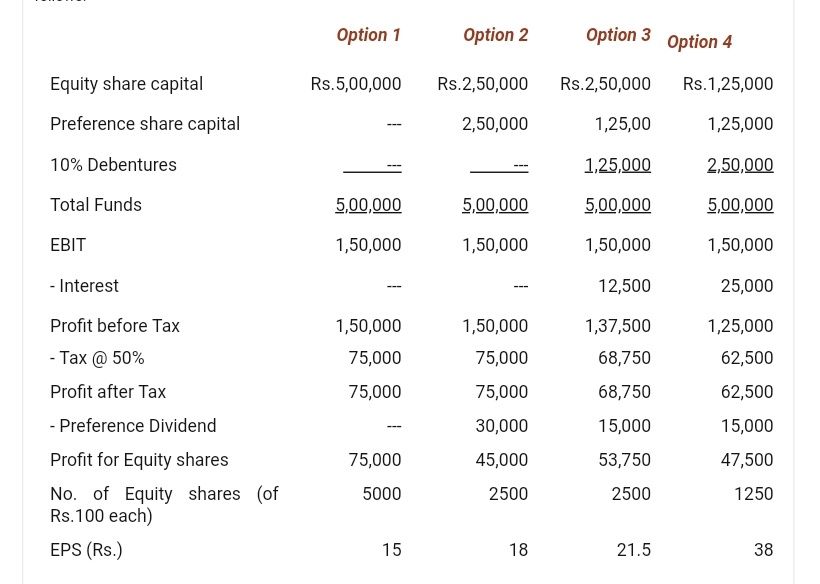
EPS in different debt-equity ratios. Source – www.sol.du.ac.in
Time value of money
In the finance world, time and money can often be considered as the same concept. Time value of money is a principal that states that money today has more value than the same amount of money in the future.
This concept deals with the investment factor, taking into account discount rates and years of investment.

Time value of money stands as an argument to always put money into use i.e invest it in-order-to never miss out on earning opportunities.
Optimal capital structure
Every company faces its own sets of challenges and opportunities in their respective business industries. Optimal capital structure of one company may be inappropriate for another. Every business must adequately consider all factors and decide how much of debt or equity should be employed.
The right ratio of capital structure would imply –
I. Wealth and Profit maximization of all stakeholders
II. Retained control
III.Avoidance of debt traps
The chain of decisions
Financial decisions establish the basis of the other two prime decisions taken up by a company –
I. Investment decisions
II. Dividend decisions
Capital structure of a firm not only lays out available funds but also reveals the necessary Return on Investment required for the company to meet its interest commitments.
Dividend decisions in-turn influence the value of the company. A company offering high dividends is viewed as a growing opportunity in the share market. This in-turn increases the value of the share, using the demand factor of the market, therefore increasing the value of the equity and firm.
Financial decisions dictate the outline of dividend decisions, influencing the payout ratio of the firm.
