Wireless Power Transmission
May 13, 2019 • 21 views
Transmission of electrical energy from source to load without having any physical wired connection, i.e. wireless power transmission will play significant role in future electronics and electrical applications. This paper discusses about wireless power transmission, principles, advantages and its scope in future.
There is an unsolved problem over a century, Wireless Power Transmission (WPT). It all started in last decades of 19th century, as we know, Nicolas Tesla was the first to propose and work on Wireless Power transmission. He demonstrated Wireless bulbs at World Columbian Exposition in early 1890s. In early 1961s William C Brown proposed possibilities of microwave power transmission. In 2007 a team from MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) has achieved to light a 60W bulb at a distance of 2 meters with ~40% efficiency. Recent years so many experiments and advancements are being happening on WPT. Different wireless mobile chargers are results of these experiments.
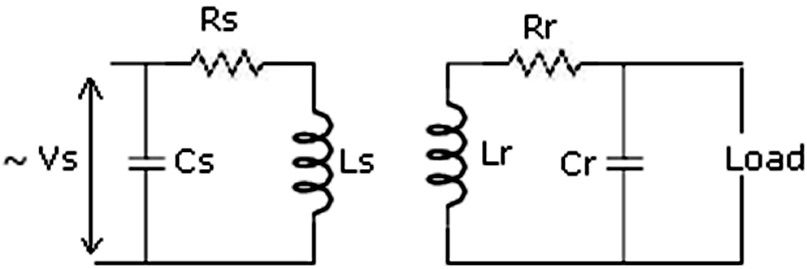
Figure 1: Simple Transmitter and Receiver circuits
Practicality of WPT:
Induction Method
Induction charging usually called as wireless charging. This technology is used to manufacture wireless charges for toothbrushes, mobiles, shavers and portable devices. Wireless charging uses same principle as transformer where there is no direct connection between primary and secondary coils. Mutual induction makes the energy transfer between primary and secondary circuits. Similarly induction coil on the charger acts as primary coil and makes alternating electromagnetic field when power is supplied to it. Secondary coil on the portable device (which needs to be charged) receives power from this electromagnetic field when it is placed on the charger and converts it to electrical current and charges the battery. This amazing principle is applied to charge devices with very small range.
It is advantageous as there are no hazardous conductors are exposed, so no risk of electrical shock and it is convenient and safe. Same principle with resonant inductive coupling can be used for power transmission. Resonant inductive coupling increases the transmission range. Here, primary and secondary coils resonate at same frequency. Electricity given to the primary coil produces oscillating current generates oscillating magnetic field and is picked up by secondary coil which is converted into electricity for the load.
Another type of coupling capacitive coupling or is electrostatic induction. Principle is capacitive coupling between two or more electrodes or plates with high frequency, high potential AC current.
All above principles are limited to small distances. These technologies can’t be implemented for larger distances.
Microwave Power Transmission
Through this method power can be transmitted over greater distances. William C Brown demonstrated wireless power transmission through microwaves using Rectenna in 1964. Rectenna is an antenna with rectifier device. Microwave power transmission gives us feasibility of directional power transmission. Typically, this system contains microwave transmitter which generates microwaves using an antenna. Receiver contains a Rectenna which converts microwaves back to electricity. One of the major obstacles with this method is it needs very large scale antennas
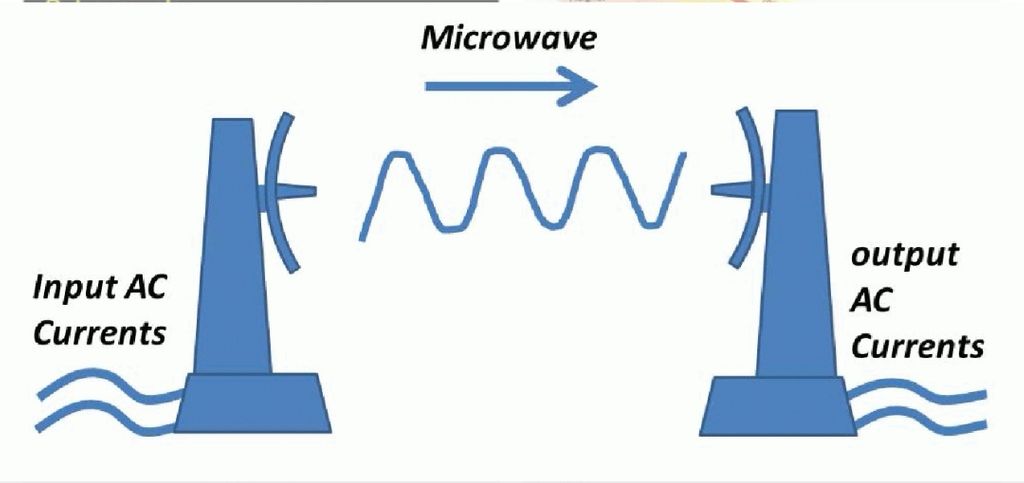
Wireless power is future and will replace existing wired communication of electricity
